2021 Vue面试题
1.函数组件的优势及原理
函数式组件的特性:无状态、无生命周期、无this。但是性能高 正常组件是一个类继承了Vue, 函数式组件就是普通的函数,没有new的过程,也没有
init、prepatchsrc/vdom/create-component.js:163if (isTrue(Ctor.options.functional)) { // 函数式组件 return createFunctionalComponent(Ctor, propsData, data, context, children) } // extract listeners, since these needs to be treated as // child component listeners instead of DOM listeners const listeners = data.on // 处理事件 // replace with listeners with .native modifier // so it gets processed during parent component patch. data.on = data.nativeOn // 处理原生事件 // install component management hooks onto the placeholder node installComponentHooks(data) // 初始化组件钩子方法1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
2.Vue组件间传值的方式及之间区别
props和$emit父组件向子组件传递数据是通过prop传递的,子组件传递数据给父组件是通过$emit触发事件来做到的$parent,$children获取当前组件的父组件和当前组件的子组件$attrs和$listenersA->B->C。Vue 2.4 开始提供了$attrs和$listeners来解决这个问题- 父组件中通过
provide来提供变量,然后在子组件中通过inject来注入变量。 $refs获取实例envetBus平级组件数据传递 这种情况下可以使用中央事件总线的方式vuex状态管理- ...
1).props实现原理
<my-component a="1" b="2" c="3" @xxx @qqq @click.native></my-component>
src\core\vdom\create-component.js:192
const vnode = new VNode( // 创建组件虚拟节点
`vue-component-${Ctor.cid}${name ? `-${name}` : ''}`,
data, undefined, undefined, undefined, context,
{ Ctor, propsData, listeners, tag, children }, // 包含组件的属性及事件
asyncFactory
)
2
3
4
5
6
src\core\instance\init.js:36
export function initInternalComponent (vm: Component, options: InternalComponentOptions) {
const opts = vm.$options = Object.create(vm.constructor.options)
// doing this because it's faster than dynamic enumeration.
const parentVnode = options._parentVnode
opts.parent = options.parent
opts._parentVnode = parentVnode
const vnodeComponentOptions = parentVnode.componentOptions
opts.propsData = vnodeComponentOptions.propsData // 将属性添加到$options中
opts._parentListeners = vnodeComponentOptions.listeners
opts._renderChildren = vnodeComponentOptions.children
opts._componentTag = vnodeComponentOptions.tag
if (options.render) {
opts.render = options.render
opts.staticRenderFns = options.staticRenderFns
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
src\core\instance\state.js属性的初始化
function initProps (vm: Component, propsOptions: Object) { // propsOptions 校验属性
const propsData = vm.$options.propsData || {} // 获取用户的数据
const props = vm._props = {}
// cache prop keys so that future props updates can iterate using Array
// instead of dynamic object key enumeration.
const keys = vm.$options._propKeys = []
const isRoot = !vm.$parent
// root instance props should be converted
if (!isRoot) { // 如果时根元素,属性需要定义成响应式的
toggleObserving(false)
}
for (const key in propsOptions) {// 用户用户的 props:{}
keys.push(key)
const value = validateProp(key, propsOptions, propsData, vm)
/* istanbul ignore else */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
const hyphenatedKey = hyphenate(key)
if (isReservedAttribute(hyphenatedKey) ||
config.isReservedAttr(hyphenatedKey)) {
warn(
`"${hyphenatedKey}" is a reserved attribute and cannot be used as component prop.`,
vm
)
}
defineReactive(props, key, value, () => {
if (!isRoot && !isUpdatingChildComponent) {
warn(
`Avoid mutating a prop directly since the value will be ` +
`overwritten whenever the parent component re-renders. ` +
`Instead, use a data or computed property based on the prop's ` +
`value. Prop being mutated: "${key}"`,
vm
)
}
})
} else {
defineReactive(props, key, value) // 定义到_props中
}
// static props are already proxied on the component's prototype
// during Vue.extend(). We only need to proxy props defined at
// instantiation here.
if (!(key in vm)) {
proxy(vm, `_props`, key) // 将_props代理到实例上
}
}
toggleObserving(true)
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
2).$on , $emit
<my-component @change="fn" @change="fn" @change="fn"></my-component> // this.$on('change')
<script>
this.$emit('change')
</script>
2
3
4
opts._parentListeners = vnodeComponentOptions.listeners // 用户在组件上定义的事件
src\core\instance\events.js:12
export function initEvents (vm: Component) {
vm._events = Object.create(null)
vm._hasHookEvent = false
// init parent attached events
const listeners = vm.$options._parentListeners
if (listeners) {
updateComponentListeners(vm, listeners) // 更新组件的事件
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
export function updateComponentListeners (
vm: Component,
listeners: Object,
oldListeners: ?Object
) {
target = vm // 更新事件,采用add 、 remove方法
updateListeners(listeners, oldListeners || {}, add, remove, createOnceHandler, vm)
target = undefined
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
function add (event, fn) {
target.$on(event, fn)
}
function remove (event, fn) {
target.$off(event, fn)
}
2
3
4
5
6
内部采用的就是发布订阅模式来进行实现
3).$parent,$children
src\core\instance\lifecycle.js:32
export function initLifecycle (vm: Component) {
const options = vm.$options
// locate first non-abstract parent
let parent = options.parent
if (parent && !options.abstract) { // 排除抽象组件
while (parent.$options.abstract && parent.$parent) {
parent = parent.$parent
}
parent.$children.push(vm) // 让父实例记住当前组件实例
}
vm.$parent = parent // 增加$parent属性 指向父实例
vm.$root = parent ? parent.$root : vm
// ...
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
4).$attrs, $listeners
<my-component a="1" b="2"></my-component> => $vnode.data.attrs = {a:1,b:2}
export function initRender (vm: Component) {
vm._vnode = null // the root of the child tree
vm._staticTrees = null // v-once cached trees
const options = vm.$options
const parentVnode = vm.$vnode = options._parentVnode // the placeholder node in parent tree 获取占位符节点
// ...
const parentData = parentVnode && parentVnode.data // 占位符节点上的数据
defineReactive(vm, '$attrs', parentData && parentData.attrs || emptyObject, null, true)
defineReactive(vm, '$listeners', options._parentListeners || emptyObject, null, true)
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
5).provide & inject
src\core\instance\inject.js:7
export function initProvide (vm: Component) {
const provide = vm.$options.provide
if (provide) { // 将用户定义的provide 挂载到_provided
vm._provided = typeof provide === 'function'
? provide.call(vm)
: provide
}
}
export function initInjections (vm: Component) { // inject:[a,b,c]
const result = resolveInject(vm.$options.inject, vm) // 不停的向上查找 inject的属性
if (result) {
toggleObserving(false)
Object.keys(result).forEach(key => {
/* istanbul ignore else */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
defineReactive(vm, key, result[key], () => {
warn(
`Avoid mutating an injected value directly since the changes will be ` +
`overwritten whenever the provided component re-renders. ` +
`injection being mutated: "${key}"`,
vm
)
})
} else {
defineReactive(vm, key, result[key])
}
})
toggleObserving(true)
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
6).$ref
src\core\vdom\modules\ref.js:20
export function registerRef (vnode: VNodeWithData, isRemoval: ?boolean) {
const key = vnode.data.ref // 获取ref
if (!isDef(key)) return
const vm = vnode.context
const ref = vnode.componentInstance || vnode.elm // 当前组件的实例 或者 组件的真实节点
const refs = vm.$refs
if (isRemoval) { // 删除ref
if (Array.isArray(refs[key])) {
remove(refs[key], ref)
} else if (refs[key] === ref) {
refs[key] = undefined
}
} else {
if (vnode.data.refInFor) {
if (!Array.isArray(refs[key])) { // 在v-for中是数组
refs[key] = [ref]
} else if (refs[key].indexOf(ref) < 0) {
// $flow-disable-line
refs[key].push(ref)
}
} else {
refs[key] = ref
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
3.$attrs是为了解决什么问题出现的,provide和inject不能解决它能解决的问题吗? v-bind="$attrs" v-on="$listeners"
$attrs主要的作用就是实现批量传递数据。provide/inject更适合应用在插件中,主要是实现跨级数据传递
4.v-if和v-for哪个优先级更高?
- v-for和v-if不要在同一个标签中使用,因为解析时先解析v-for在解析v-if。如果遇到需要同时使用时可以考虑写成计算属性的方式。
src/compiler/index.js:19
src/compiler/codegen/index.js::56解析v-if 和 v-for
if (el.staticRoot && !el.staticProcessed) {
return genStatic(el, state)
} else if (el.once && !el.onceProcessed) {
return genOnce(el, state)
} else if (el.for && !el.forProcessed) { // 处理v-for
return genFor(el, state)
} else if (el.if && !el.ifProcessed) { // 处理v-if
return genIf(el, state)
} else if (el.tag === 'template' && !el.slotTarget && !state.pre) {
return genChildren(el, state) || 'void 0'
} else if (el.tag === 'slot') {
return genSlot(el, state)
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
5.v-if,v-model,v-for的实现原理
v-for实现原理src/compiler/codegen/index.js:187export function genFor( el: any, state: CodegenState, altGen ? : Function, altHelper ? : string ): string { const exp = el.for // 拿到表达式arr const alias = el.alias const iterator1 = el.iterator1 ? `,${el.iterator1}` : '' const iterator2 = el.iterator2 ? `,${el.iterator2}` : '' if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && state.maybeComponent(el) && // slot 和 template不能进行v-for操作 el.tag !== 'slot' && el.tag !== 'template' && !el.key ) { state.warn( `<${el.tag} v-for="${alias} in ${exp}">: component lists rendered with ` + `v-for should have explicit keys. ` + `See https://vuejs.org/guide/list.html#key for more info.`, el.rawAttrsMap['v-for'], true /* tip */ ) } el.forProcessed = true // avoid recursion 生成循环函数 const r = `${altHelper || '_l'}((${exp}),` + `function(${alias}${iterator1}${iterator2}){` + `return ${(altGen || genElement)(el, state)}` + '})' return r; }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33v-if实现原理src/compiler/codegen/index.js:147function genIfConditions( conditions: ASTIfConditions, state: CodegenState, altGen ? : Function, altEmpty ? : string ): string { if (!conditions.length) { return altEmpty || '_e()' } const condition = conditions.shift() if (condition.exp) { // 如果有表达式 return `(${condition.exp})?${ // 将表达式拼接起来 genTernaryExp(condition.block) }:${ // v-else-if genIfConditions(conditions, state, altGen, altEmpty) }` } else { return `${genTernaryExp(condition.block)}` // 没有表达式直接生成元素 像v-else } // v-if with v-once should generate code like (a)?_m(0):_m(1) function genTernaryExp(el) { return altGen ? altGen(el, state) : el.once ? genOnce(el, state) : genElement(el, state) } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29v-model实现原理普通元素上的v-model指令
src/compiler/codegen/index.js:310
function genDirectives(el: ASTElement, state: CodegenState): string | void { const dirs = el.directives // 获取所有指令 if (!dirs) return let res = 'directives:[' let hasRuntime = false let i, l, dir, needRuntime for (i = 0, l = dirs.length; i < l; i++) { dir = dirs[i] needRuntime = true const gen: DirectiveFunction = state.directives[dir.name] if (gen) { // compile-time directive that manipulates AST. // returns true if it also needs a runtime counterpart. needRuntime = !!gen(el, dir, state.warn) // 添加input事件 和 value属性 } if (needRuntime) { hasRuntime = true // 是否需要运行时 res += `{name:"${dir.name}",rawName:"${dir.rawName}"${ dir.value ? `,value:(${dir.value}),expression:${JSON.stringify(dir.value)}` : '' }${ dir.arg ? `,arg:${dir.isDynamicArg ? dir.arg : `"${dir.arg}"`}` : '' }${ dir.modifiers ? `,modifiers:${JSON.stringify(dir.modifiers)}` : '' }},` } } if (hasRuntime) { // directives:[{name:"model",rawName:"v-model",value:(msg),expression:"msg"}] 生成对应指令 let result = res.slice(0, -1) + ']' return result; } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31组件上的v-model指令
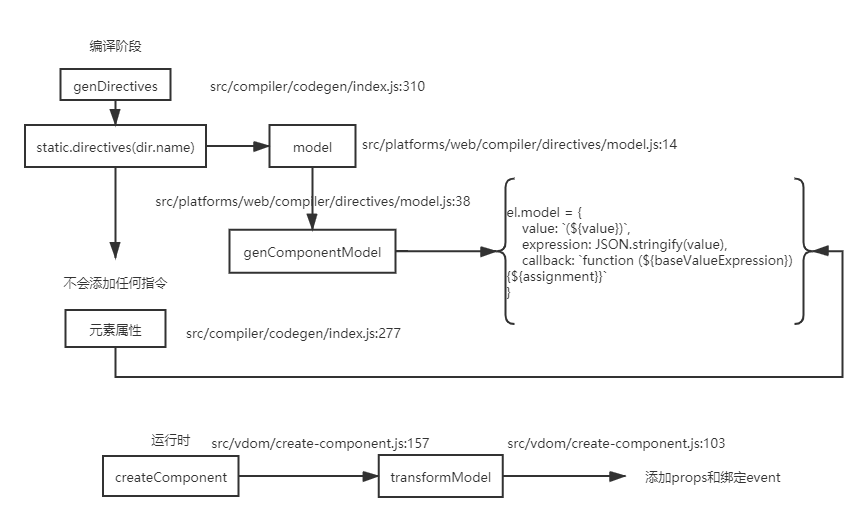
function transformModel (options, data: any) { const prop = (options.model && options.model.prop) || 'value' // 默认采用value属性 const event = (options.model && options.model.event) || 'input' // 默认采用input事件 ;(data.attrs || (data.attrs = {}))[prop] = data.model.value // 绑定属性 const on = data.on || (data.on = {}) // 绑定事件 const existing = on[event] const callback = data.model.callback if (isDef(existing)) { if ( Array.isArray(existing) ? existing.indexOf(callback) === -1 : existing !== callback ) { on[event] = [callback].concat(existing) } } else { on[event] = callback } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
6.Vue中slot是如何实现的?什么时候使用它?
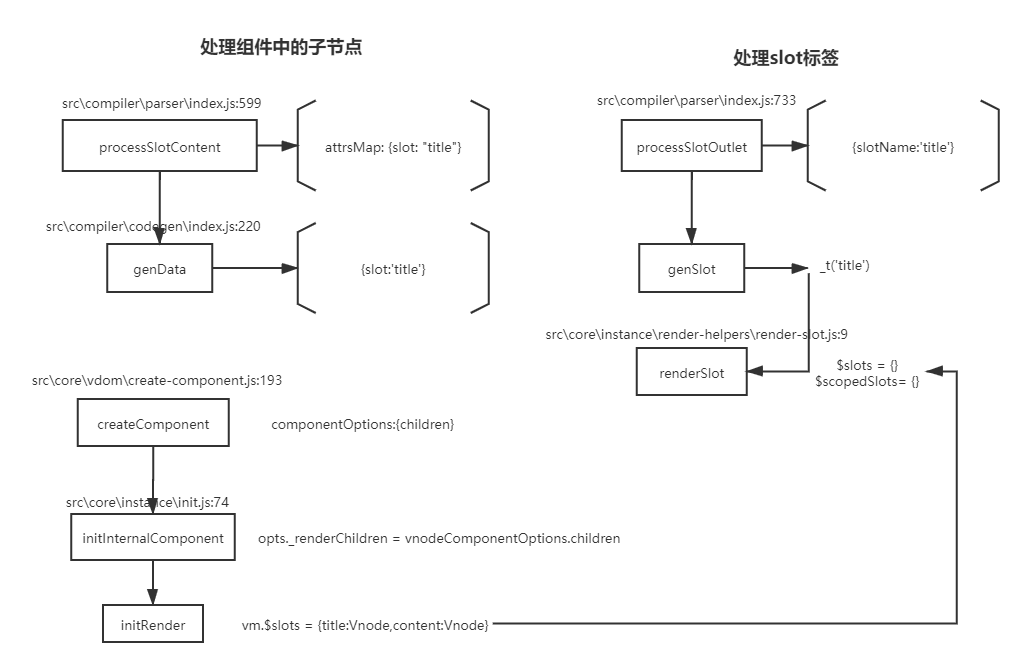
const templateCompiler = require('vue-template-compiler');
let r = templateCompiler.compile(`
<div>
<slot name="title"></slot>
<slot name="content"></slot>
</div>`);
// with(this){return _c('div',[_t("title"),_v(" "),_t("content")],2)}
console.log(r.render)
let r1 = templateCompiler.compile(`
<my>
<h1 slot="title">标题</h1>
<div slot="content">内容</div>
</my>`)
/**
with(this){
return _c('my',[
_c('h1',{attrs:{"slot":"title"},slot:"title"},[_v("标题")]),_v(" "),
_c('div',{attrs:{"slot":"content"},slot:"content"},[_v("内容")])
])
}
**/
console.log(r1.render)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
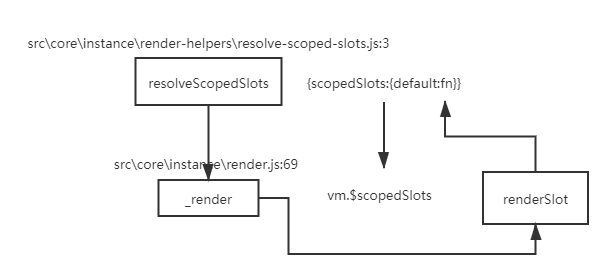
let r3 = templateCompiler.compile(`
<div>
<slot :article="{title:'标题',content:'内容'}"></slot>
</div>`);
// with(this){return _c('div',[_t("default",null,{"article":{title:'标题',content:'内容'}})],2)}
console.log(r3.render)
let r4 = templateCompiler.compile(`
<my>
<template slot-scope="{article}">
<h1 slot="article.title">标题</h1>
<div slot="article.content">内容</div>
</template>
</my>`)
/**
with(this){return _c('my',
{scopedSlots:_u([
{key:"default",fn:function({article}){
return [
_c('h1',{attrs:{"slot":"article.title"},slot:"article.title"},[_v("标题")]),
_v(" "),
_c('div',{attrs:{"slot":"article.content"},slot:"article.content"},[_v("内容")])
]
}
}
])
})}
*/
console.log(r4.render)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
普通插槽,渲染在父级, 作用域插槽在组件内部渲染!
7.Vue.use是干什么的?原理是什么?
Vue.use是用来使用插件的,我们可以在插件中扩展全局组件、指令、原型方法等。- 会调用插件的
install方法,将Vue的构造函数默认传入,这样在插件中可以使用Vue无需依赖Vue库
src/core/global-api/use.js
Vue.use = function (plugin: Function | Object) {
// 插件缓存
const installedPlugins = (this._installedPlugins || (this._installedPlugins = []))
if (installedPlugins.indexOf(plugin) > -1) { // 如果已经有插件 直接返回
return this
}
// additional parameters
const args = toArray(arguments, 1) // 除了第一项其他的参数整合成数组
args.unshift(this) // 将Vue 放入到数组中
if (typeof plugin.install === 'function') { // 调用install方法
plugin.install.apply(plugin, args)
} else if (typeof plugin === 'function') { // 直接调用方法
plugin.apply(null, args)
}
installedPlugins.push(plugin) // 缓存插件
return this
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
8.组件中写name选项有哪些好处及作用?
- 增加name选项会在
components属性中增加组件本身,实现组件的递归调用。 - 可以标识组件的具体名称方便调试和查找对应组件。
src/core/global-api/extend.js:67
Sub.options.components[name] = Sub
9.Vue事件修饰符有哪些?其实现原理是什么?
- .stop、.prevent、.capture!、.self、.once~、.passive&
src\compiler\helpers.js:69
export function addHandler (
el: ASTElement,
name: string,
value: string,
modifiers: ?ASTModifiers,
important?: boolean,
warn?: ?Function,
range?: Range,
dynamic?: boolean
) {
modifiers = modifiers || emptyObject
// warn prevent and passive modifier
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (
process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && warn &&
modifiers.prevent && modifiers.passive
) {
warn(
'passive and prevent can\'t be used together. ' +
'Passive handler can\'t prevent default event.',
range
)
}
if (modifiers.right) {
if (dynamic) {
name = `(${name})==='click'?'contextmenu':(${name})`
} else if (name === 'click') {
name = 'contextmenu'
delete modifiers.right
}
} else if (modifiers.middle) {
if (dynamic) {
name = `(${name})==='click'?'mouseup':(${name})`
} else if (name === 'click') {
name = 'mouseup'
}
}
// check capture modifier
if (modifiers.capture) { // 如果capture 用!标记
delete modifiers.capture
name = prependModifierMarker('!', name, dynamic)
}
if (modifiers.once) { // 如果是once 用~ 标记
delete modifiers.once
name = prependModifierMarker('~', name, dynamic)
}
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (modifiers.passive) { // 如果是passive 用 &标记
delete modifiers.passive
name = prependModifierMarker('&', name, dynamic)
}
let events
if (modifiers.native) {
delete modifiers.native
events = el.nativeEvents || (el.nativeEvents = {})
} else {
events = el.events || (el.events = {})
}
const newHandler: any = rangeSetItem({ value: value.trim(), dynamic }, range)
if (modifiers !== emptyObject) {
newHandler.modifiers = modifiers
}
const handlers = events[name]
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (Array.isArray(handlers)) {
important ? handlers.unshift(newHandler) : handlers.push(newHandler)
} else if (handlers) {
events[name] = important ? [newHandler, handlers] : [handlers, newHandler]
} else {
events[name] = newHandler
}
el.plain = false
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
src\compiler\codegen\events.js:42
function genHandler (handler: ASTElementHandler | Array<ASTElementHandler>): string {
let code = ''
let genModifierCode = ''
const keys = []
for (const key in handler.modifiers) {
if (modifierCode[key]) {
genModifierCode += modifierCode[key]
// left/right
if (keyCodes[key]) {
keys.push(key)
}
} else if (key === 'exact') {
const modifiers: ASTModifiers = (handler.modifiers: any)
genModifierCode += genGuard(
['ctrl', 'shift', 'alt', 'meta']
.filter(keyModifier => !modifiers[keyModifier])
.map(keyModifier => `$event.${keyModifier}Key`)
.join('||')
)
} else {
keys.push(key) // modifiers中表达式存起来
}
}
if (keys.length) {
code += genKeyFilter(keys)
}
// Make sure modifiers like prevent and stop get executed after key filtering
if (genModifierCode) {
code += genModifierCode
}
const handlerCode = isMethodPath
? `return ${handler.value}.apply(null, arguments)`
: isFunctionExpression
? `return (${handler.value}).apply(null, arguments)`
: isFunctionInvocation
? `return ${handler.value}`
: handler.value
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (__WEEX__ && handler.params) {
return genWeexHandler(handler.params, code + handlerCode)
}
return `function($event){${code}${handlerCode}}`
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
vue-dev\src\platforms\web\runtime\modules\events.js:105
export function updateListeners (
on: Object,
oldOn: Object,
add: Function,
remove: Function,
createOnceHandler: Function,
vm: Component
) {
let name, def, cur, old, event
for (name in on) { // 循环on中的 即事件
def = cur = on[name]
old = oldOn[name]
event = normalizeEvent(name) // 事件修饰符
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (__WEEX__ && isPlainObject(def)) {
cur = def.handler
event.params = def.params
}
if (isUndef(cur)) {
process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && warn(
`Invalid handler for event "${event.name}": got ` + String(cur),
vm
)
} else if (isUndef(old)) {
if (isUndef(cur.fns)) {
cur = on[name] = createFnInvoker(cur, vm)
}
if (isTrue(event.once)) {
cur = on[name] = createOnceHandler(event.name, cur, event.capture)
}
add(event.name, cur, event.capture, event.passive, event.params)
} else if (cur !== old) {
old.fns = cur
on[name] = old
}
}
for (name in oldOn) {
if (isUndef(on[name])) {
event = normalizeEvent(name)
remove(event.name, oldOn[name], event.capture)
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
10.Vue中.sync修饰符的作用,用法及实现原理
src\compiler\parser\index.js:798
if (modifiers.sync) {
syncGen = genAssignmentCode(value, `$event`) // 转.async 改成 ${value} = xxx
if (!isDynamic) {
addHandler( // 添加update事件
el,
`update:${camelize(name)}`,
syncGen,
null,
false,
warn,
list[i]
)
if (hyphenate(name) !== camelize(name)) {
addHandler(
el,
`update:${hyphenate(name)}`,
syncGen,
null,
false,
warn,
list[i]
)
}
} else {
// handler w/ dynamic event name
addHandler(
el,
`"update:"+(${name})`,
syncGen,
null,
false,
warn,
list[i],
true // dynamic
)
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
let r5 = templateCompiler.compile(`
<my :value.sync="xxxx"></my>
`);
// with(this){return _c('my',{attrs:{"value":xxxx},on:{"update:value":function($event){xxxx=$event}}})}
console.log(r5.render)
2
3
4
5
6
11.如何理解自定义指令
1.在生成
ast语法树时,遇到指令会给当前元素添加directives属性2.通过
genDeirectives生成指令代码3.在
patch前将指令的钩子提取到cbs中,在patch过程中调用对应的钩子4.当执行
cbs对应的钩子时,调用对应指令定义的方法src/vdom/patch.js:77提取钩子函数const hooks = ['create', 'activate', 'update', 'remove', 'destroy'] const { modules, nodeOps } = backend for (i = 0; i < hooks.length; ++i) { cbs[hooks[i]] = [] for (j = 0; j < modules.length; ++j) { if (isDef(modules[j][hooks[i]])) { cbs[hooks[i]].push(modules[j][hooks[i]]); // 收集hook,patch过程中调用 // {create:[fn,fn],activate:[fn,fn]...} } } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11src/vdom/modules/directives.js:7指令钩子export default { // 指令的钩子, 在创建和更新过程中会调用 create、update、destroy钩子 create: updateDirectives, update: updateDirectives, destroy: function unbindDirectives (vnode: VNodeWithData) { updateDirectives(vnode, emptyNode) } } function updateDirectives (oldVnode: VNodeWithData, vnode: VNodeWithData) { if (oldVnode.data.directives || vnode.data.directives) { // 如果有指令 _update(oldVnode, vnode) } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
12.keep-alive平时在哪里使用?原理是?
- 使用keep-alive包裹动态组件时, 会对组件进行缓存。避免组件的重新创建
<keep-alive :include="whiteList" :exclude="blackList" :max="count">
<component :is="component"></component>
</keep-alive>
2
3
<keep-alive :include="whiteList" :exclude="blackList" :max="count">
<router-view></router-view>
</keep-alive>
2
3
实现原理
export default { name: 'keep-alive', abstract: true, // 不会放到对应的lifecycle props: { include: patternTypes, // 白名单 exclude: patternTypes, // 黑名单 max: [String, Number] // 缓存的最大个数 }, created () { this.cache = Object.create(null) // 缓存列表 this.keys = [] // 缓存的key列表 }, destroyed () { for (const key in this.cache) { // keep-alive销毁时 删除所有缓存 pruneCacheEntry(this.cache, key, this.keys) } }, mounted () { // 监控缓存列表 this.$watch('include', val => { pruneCache(this, name => matches(val, name)) }) this.$watch('exclude', val => { pruneCache(this, name => !matches(val, name)) }) }, render () { const slot = this.$slots.default const vnode: VNode = getFirstComponentChild(slot) 、// 获得第一个组件 const componentOptions: ?VNodeComponentOptions = vnode && vnode.componentOptions if (componentOptions) { // check pattern const name: ?string = getComponentName(componentOptions) const { include, exclude } = this if ( // 获取组件名 看是否需要缓存,不需要缓存则直接返回 // not included (include && (!name || !matches(include, name))) || // excluded (exclude && name && matches(exclude, name)) ) { return vnode } const { cache, keys } = this const key: ?string = vnode.key == null // same constructor may get registered as different local components // so cid alone is not enough (#3269) ? componentOptions.Ctor.cid + (componentOptions.tag ? `::${componentOptions.tag}` : '') : vnode.key // 生成缓存的key if (cache[key]) { // 如果有key 将组件实例直接复用 vnode.componentInstance = cache[key].componentInstance // make current key freshest remove(keys, key) keys.push(key) // lru算法 } else { cache[key] = vnode // 缓存组件 keys.push(key) // prune oldest entry if (this.max && keys.length > parseInt(this.max)) { pruneCacheEntry(cache, keys[0], keys, this._vnode) // 超过最大限制删除第一个 } } vnode.data.keepAlive = true // 在firstComponent的vnode中增加keep-alive属性 } return vnode || (slot && slot[0]) } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72keep-alive第一次渲染的时候,会将其第一个子组件,缓存起来。- 当组件后续在次被激活时,会复用上一次缓存的实例进行渲染。
src\core\vdom\patch.js:210function createComponent (vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, parentElm, refElm) { let i = vnode.data if (isDef(i)) { const isReactivated = isDef(vnode.componentInstance) && i.keepAlive if (isDef(i = i.hook) && isDef(i = i.init)) { i(vnode, false /* hydrating */) } if (isDef(vnode.componentInstance)) { initComponent(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue) insert(parentElm, vnode.elm, refElm) // 将原来的elm,插入到页面中 if (isTrue(isReactivated)) { reactivateComponent(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, parentElm, refElm) } return true } } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17src\core\vdom\create-component.js:36const componentVNodeHooks = { init (vnode: VNodeWithData, hydrating: boolean): ?boolean { if ( vnode.componentInstance && !vnode.componentInstance._isDestroyed && vnode.data.keepAlive // 有keepAlive, 不在执行组件的初始化流程 ) { // kept-alive components, treat as a patch const mountedNode: any = vnode // work around flow componentVNodeHooks.prepatch(mountedNode, mountedNode) } else { const child = vnode.componentInstance = createComponentInstanceForVnode( vnode, activeInstance ) // 组件挂载 当前组件实例中 包含$el属性 child.$mount(hydrating ? vnode.elm : undefined, hydrating) } } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
13.Vue-Router有几种钩子函数,具体是什么及执行流程是怎样的?
钩子函数的种类有:全局守卫、路由守卫、组件守卫
- 导航被触发。
- 在失活的组件里调用
beforeRouteLeave守卫。 - 调用全局的
beforeEach守卫。 - 在重用的组件里调用
beforeRouteUpdate守卫 (2.2+)。 - 在路由配置里调用
beforeEnter。 - 解析异步路由组件。
- 在被激活的组件里调用
beforeRouteEnter。 - 调用全局的
beforeResolve守卫 (2.5+)。 - 导航被确认。
- 调用全局的
afterEach钩子。 - 触发 DOM 更新。
- 调用
beforeRouteEnter守卫中传给next的回调函数,创建好的组件实例会作为回调函数的参数传入。
const queue: Array<?NavigationGuard> = [].concat(
// in-component leave guards
extractLeaveGuards(deactivated), // 离开钩子
// global before hooks
this.router.beforeHooks, // 全局before钩子
// in-component update hooks
extractUpdateHooks(updated), // 更新钩子 beforeRouteUpdate
// in-config enter guards
activated.map(m => m.beforeEnter), // beforeEnter钩子
// async components
resolveAsyncComponents(activated) // 异步组件
)
runQueue(queue, iterator, () => {
// wait until async components are resolved before
// extracting in-component enter guards
const enterGuards = extractEnterGuards(activated) // beforeRouteEnter
const queue = enterGuards.concat(this.router.resolveHooks) // beforeResolve
runQueue(queue, iterator, () => {
afterEachs.forEach(fn=>fn())
})
})
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
14.Vue-Router的两种模式的区别
Vue-Router有三种模式hash、history、abstractabstract模式是在不支持浏览器API环境使用,不依赖于浏览器历史hash模式:hash+popState/hashChange兼容性好但是不够美观,hash服务端无法获取。不利于seo优化history模式:historyApi+popState美观,刷新会出现404 -> CLI webpack history-fallback
15.谈一下你对vuex的个人理解
vuex是专门为vue提供的全局状态管理系统,用于多个组件中数据共享、数据缓存等。(无法持久化、内部核心原理是通过创造一个全局实例new Vue)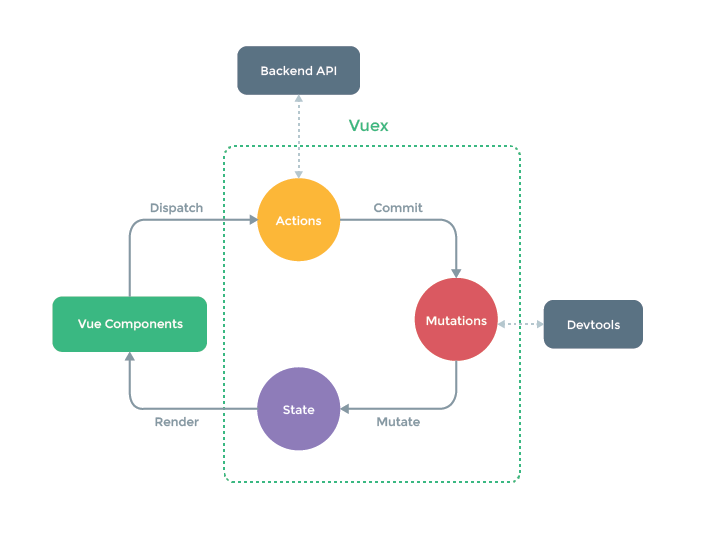
方法:
replaceState、subscribe、registerModule、namespace(modules)、辅助函数...
16.mutation和action的区别
mutation: 主要在于修改状态,必须同步执行action: 执行业务代码,方便复用,逻辑可以为异步,不能直接修改状态
function enableStrictMode (store) {
store._vm.$watch(function () { return this._data.$$state }, function () {
if ((process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production')) {
assert(store._committing, "do not mutate vuex store state outside mutation handlers.");
}
}, { deep: true, sync: true }); // 同步watcher监控状态变化
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
17.Vue中的性能优化有哪些?
数据层级不易过深,合理设置响应式数据
使用数据时缓存值的结果,不频繁取值。
合理设置Key属性
v-show和v-if的选取
控制组件粒度 -> Vue采用组件级更新
采用函数式组件 -> 函数式组件开销低
采用异步组件 -> 借助
webpack分包的能力使用
keep-alive缓存组件虚拟滚动、时间分片等策略...
打包优化
18.Vue中使用了哪些设计模式?
- 单例模式 - 单例模式就是整个程序有且仅有一个实例
export function install (_Vue) {
if (Vue && _Vue === Vue) {
if (__DEV__) {
console.error(
'[vuex] already installed. Vue.use(Vuex) should be called only once.'
)
}
return
}
Vue = _Vue
applyMixin(Vue)
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
- 工厂模式 - 传入参数即可创建实例 (
createElement)
export function _createElement (
context: Component,
tag?: string | Class<Component> | Function | Object,
data?: VNodeData,
children?: any,
normalizationType?: number
): VNode | Array<VNode> {
// ...
if (typeof tag === 'string') {
let Ctor
ns = (context.$vnode && context.$vnode.ns) || config.getTagNamespace(tag)
if (config.isReservedTag(tag)) {
vnode = new VNode(
config.parsePlatformTagName(tag), data, children,
undefined, undefined, context
)
} else if ((!data || !data.pre) && isDef(Ctor = resolveAsset(context.$options, 'components', tag))) {
vnode = createComponent(Ctor, data, context, children, tag)
} else {
vnode = new VNode(
tag, data, children,
undefined, undefined, context
)
}
} else {
vnode = createComponent(tag, data, context, children)
}
// ....
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
- 发布订阅模式 - 订阅者把自己想订阅的事件注册到调度中心,当该事件触发时候,发布者发布该事件到调度中心,由调度中心统一调度订阅者注册到调度中心的处理代码。
Vue.prototype.$on = function (event: string | Array<string>, fn: Function): Component {
const vm: Component = this
if (Array.isArray(event)) {
for (let i = 0, l = event.length; i < l; i++) {
vm.$on(event[i], fn)
}
} else {
(vm._events[event] || (vm._events[event] = [])).push(fn)
if (hookRE.test(event)) {
vm._hasHookEvent = true
}
}
return vm
}
Vue.prototype.$emit = function (event: string): Component {
const vm: Component = this
let cbs = vm._events[event]
if (cbs) {
cbs = cbs.length > 1 ? toArray(cbs) : cbs
const args = toArray(arguments, 1)
const info = `event handler for "${event}"`
for (let i = 0, l = cbs.length; i < l; i++) {
invokeWithErrorHandling(cbs[i], vm, args, vm, info)
}
}
return vm
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
观察者模式 -
watcher&dep的关系代理模式 - 代理模式给某一个对象提供一个代理对象,并由代理对象控制对原对象的引用。
_data属性、proxy、防抖、节流 let p = new Proxy
装饰模式 -
Vue2装饰器的用法 (对功能进行增强 @)中介者模式 - 中介者是一个行为设计模式,通过提供一个统一的接口让系统的不同部分进行通信。
Vuex策略模式 - 策略模式指对象有某个行为,但是在不同的场景中,该行为有不同的实现方案。 mergeOptions
外观模式 - 提供了统一的接口,用来访问子系统中的一群接口。
......