Appearance
前后元素不一致
两个不同虚拟节点不需要进行比较,直接移除老节点,将新的虚拟节点渲染成真实 DOM 进行挂载即可
export const isSameVNodeType = (n1, n2) => {
return n1.type === n2.type && n1.key === n2.key;
};
const patch = (n1, n2, container) => {
// 初始化和diff算法都在这里喲
if (n1 == n2) {
return;
}
if (n1 && !isSameVNodeType(n1, n2)) {
// 有n1 是n1和n2不是同一个节点
unmount(n1);
n1 = null;
}
if (n1 == null) {
// 初始化的情况
mountElement(n2, container);
} else {
// diff算法
}
};
const patch = (n1, n2, container) => {
// ....
processElement(n1, n2, container); // 封装对元素的处理逻辑
};
前后元素一致
前后元素一致则比较两个元素的属性和孩子节点
const patchProps = (oldProps, newProps, el) => {
for (let key in newProps) {
// 用新的生效
hostPatchProp(el, key, oldProps[key], newProps[key]);
}
// 老的里面有新的没有则删除
for (let key in oldProps) {
if (!(key in newProps)) {
hostPatchProp(el, key, oldProps[key], null);
}
}
};
const patchElement = (n1, n2) => {
let el = (n2.el = n1.el);
const oldProps = n1.props || {};
const newProps = n2.props || {};
patchProps(oldProps, newProps, el); // 比对新老属性
patchChildren(n1, n2, el); // 比较元素的孩子节点
};
const processElement = (n1, n2, container) => {
if (n1 == null) {
mountElement(n2, container);
} else {
patchElement(n1, n2); // 比较两个元素
}
};
子元素比较情况
| 新儿子 | 旧儿子 | 操作方式 |
|---|---|---|
| 文本 | 数组 | (删除老儿子,设置文本内容) |
| 文本 | 文本 | (更新文本即可) |
| 文本 | 空 | (更新文本即可) 与上面的类似 |
| 数组 | 数组 | (diff 算法) |
| 数组 | 文本 | (清空文本,进行挂载) |
| 数组 | 空 | (进行挂载) 与上面的类似 |
| 空 | 数组 | (删除所有儿子) |
| 空 | 文本 | (清空文本) |
| 空 | 空 | (无需处理) |
子节点有三种情况: 文本、数组、没有儿子
- 1.新的是文本,老的是数组移除老的;
- 2.新的是文本,老的也是文本,内容不相同替换
- 3.老的是数组,新的是数组,全量 diff 算法
- 4.老的是数组,新的不是数组,移除老的子节点
- 5.老的是文本,新的是空
- 6.老的是文本,新的是数组
const unmountChildren = (children) => {
for (let i = 0; i < children.length; i++) {
unmount(children[i]);
}
};
const patchChildren = (n1, n2, el) => {
const c1 = n1 && n1.children;
const c2 = n2.children;
const prevShapeFlag = n1.shapeFlag;
const shapeFlag = n2.shapeFlag;
if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.TEXT_CHILDREN) {
if (prevShapeFlag & ShapeFlags.ARRAY_CHILDREN) {
unmountChildren(c1);
}
if (c1 !== c2) {
hostSetElementText(el, c2);
}
} else {
if (prevShapeFlag & ShapeFlags.ARRAY_CHILDREN) {
if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.ARRAY_CHILDREN) {
} else {
unmountChildren(c1);
}
} else {
if (prevShapeFlag & ShapeFlags.TEXT_CHILDREN) {
hostSetElementText(el, "");
}
if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.ARRAY_CHILDREN) {
mountChildren(c2, el);
}
}
}
};
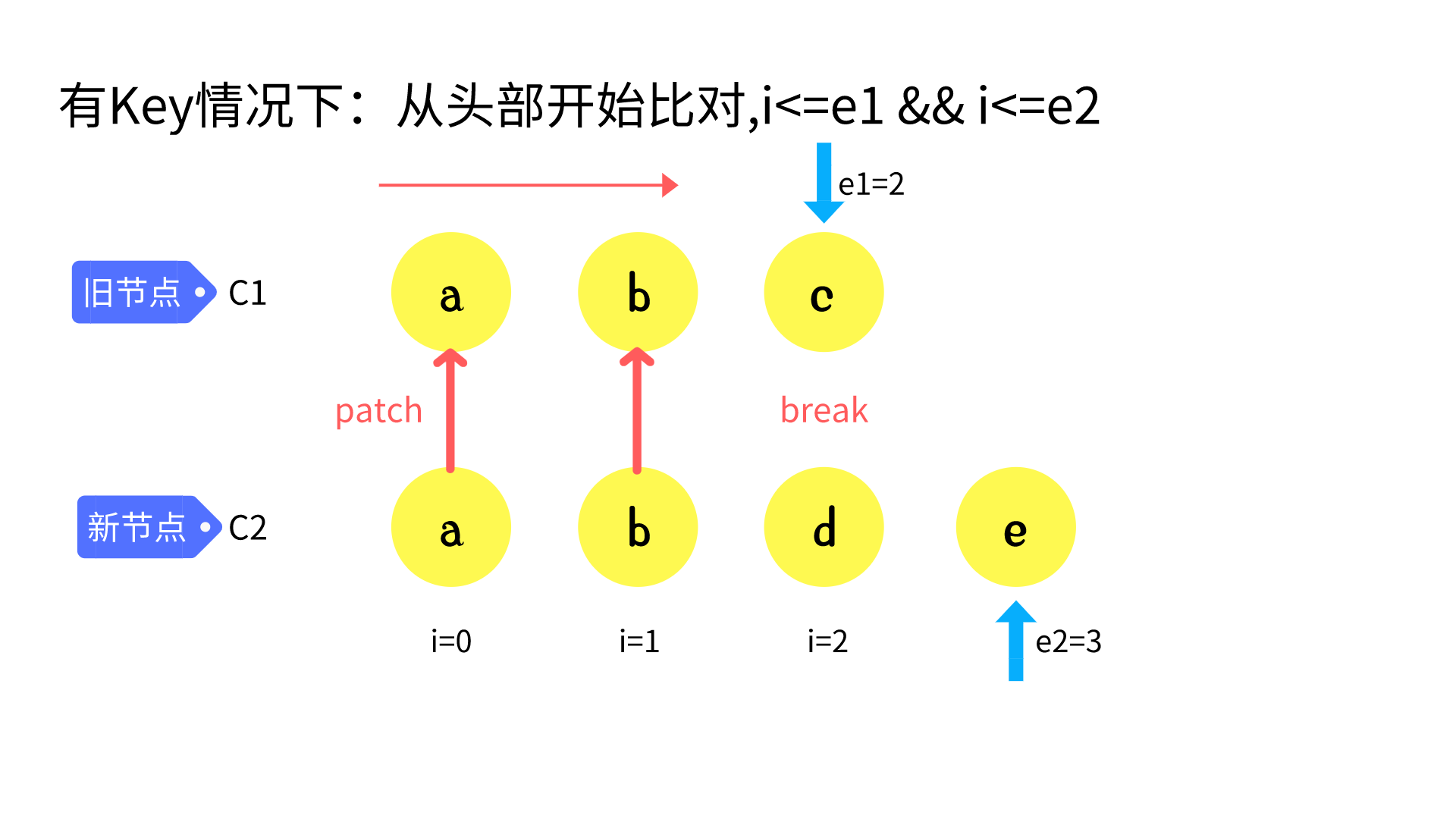
核心Diff算法
sync from start
h('div',[
h('li', { key: 'a' }, 'a'),
h('li', { key: 'b' }, 'b'),
h('li', { key: 'c' }, 'c')
]) :
h('div',[
h('li', { key: 'a' }, 'a'),
h('li', { key: 'b' }, 'b'),
h('li', { key: 'd' }, 'd'),
h('li', { key: 'e' }, 'e')
])
const patchKeydChildren = (c1, c2, container) => {
let i = 0;
const l2 = c2.length;
let e1 = c1.length - 1;
let e2 = l2 - 1;
// 1. sync from start
// (a b) c
// (a b) d e
while (i <= e1 && i <= e2) {
const n1 = c1[i];
const n2 = c2[i];
if (isSameVNodeType(n1, n2)) {
patch(n1, n2, container);
} else {
break;
}
i++;
}
};
sync from end
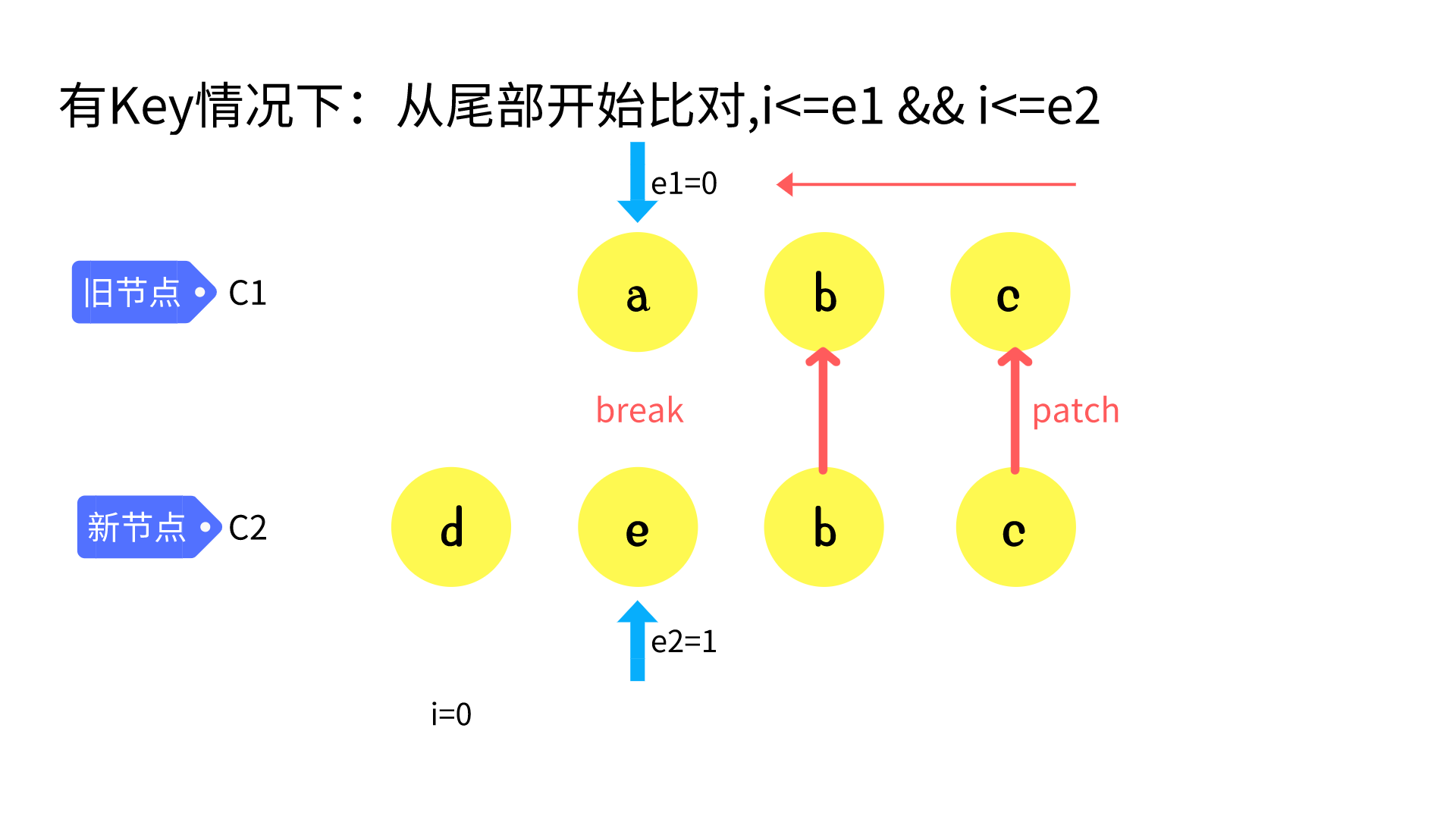
// 2. sync from end
// a (b c)
// d e (b c)
while (i <= e1 && i <= e2) {
const n1 = c1[e1];
const n2 = c2[e2];
if (isSameVNodeType(n1, n2)) {
patch(n1, n2, container);
} else {
break;
}
e1--;
e2--;
}
common sequence + mount
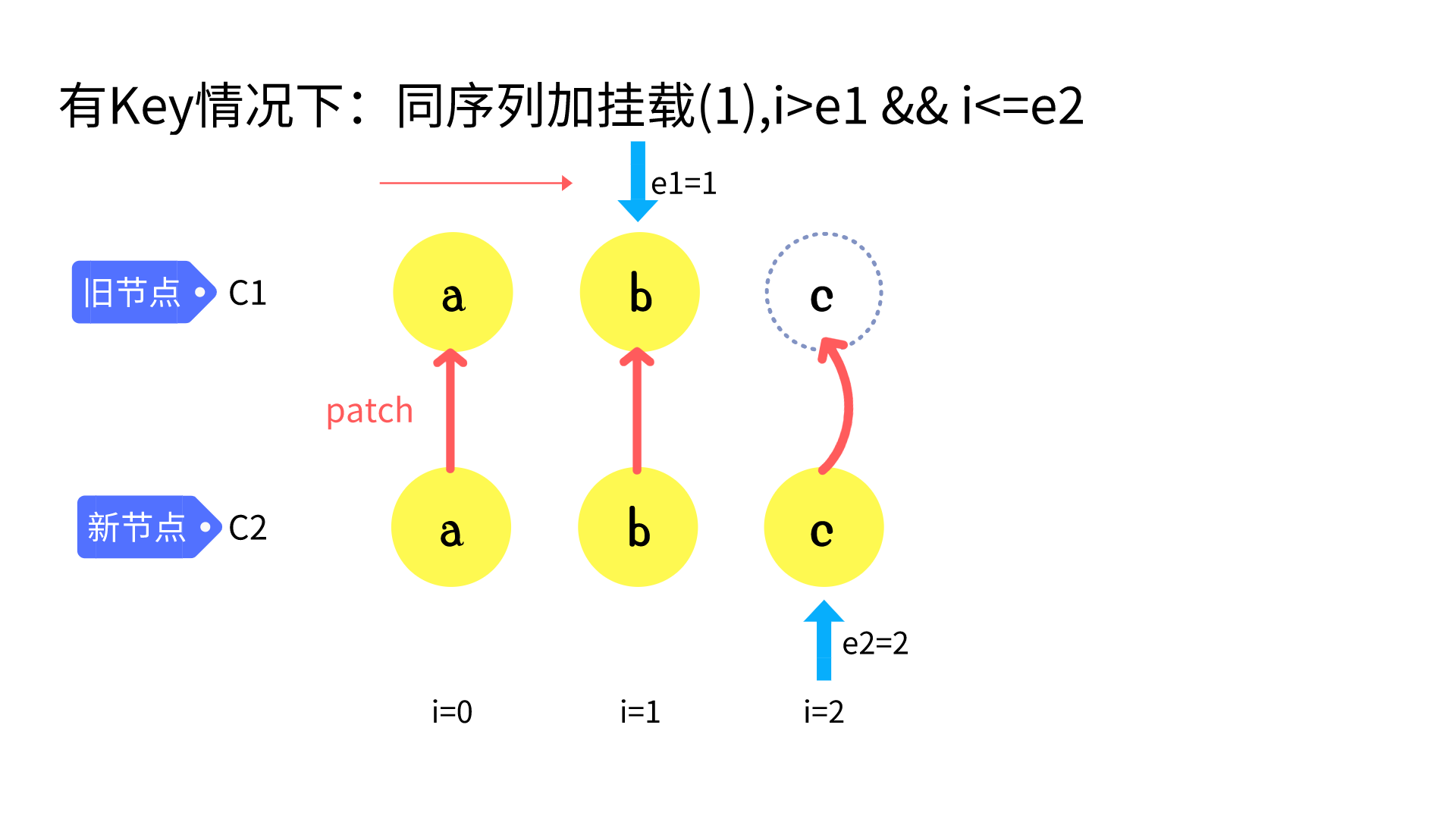
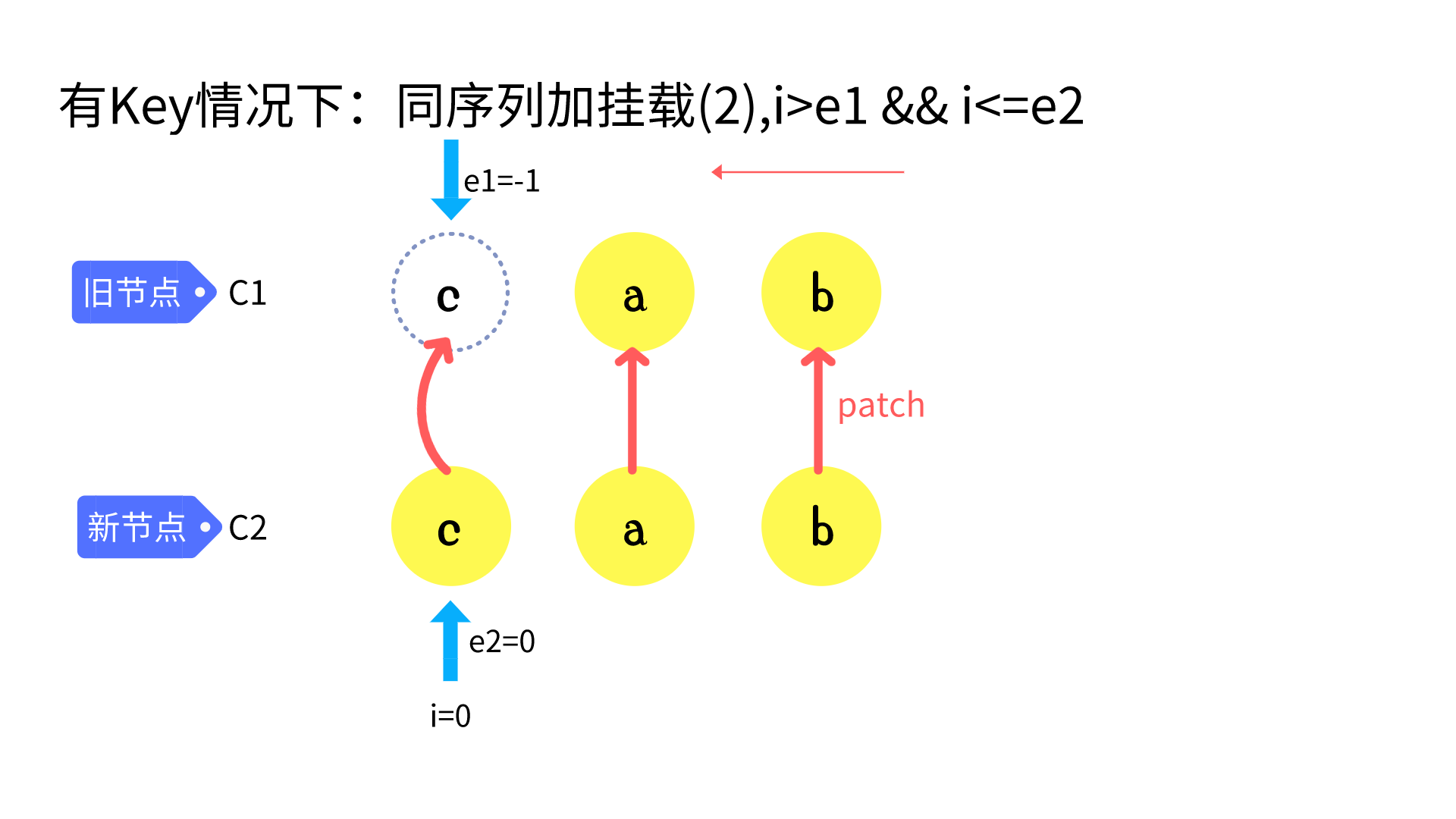
// 3. common sequence + mount
// (a b)
// (a b) c
// i = 2, e1 = 1, e2 = 2
// (a b)
// c (a b)
// i = 0, e1 = -1, e2 = 0
if (i > e1) {
// 说明有新增
if (i <= e2) {
// 表示有新增的部分
// 先根据e2 取他的下一个元素 和 数组长度进行比较
const nextPos = e2 + 1;
const anchor = nextPos < c2.length ? c2[nextPos].el : null;
while (i <= e2) {
patch(null, c2[i], container, anchor);
i++;
}
}
}
common sequence + unmount
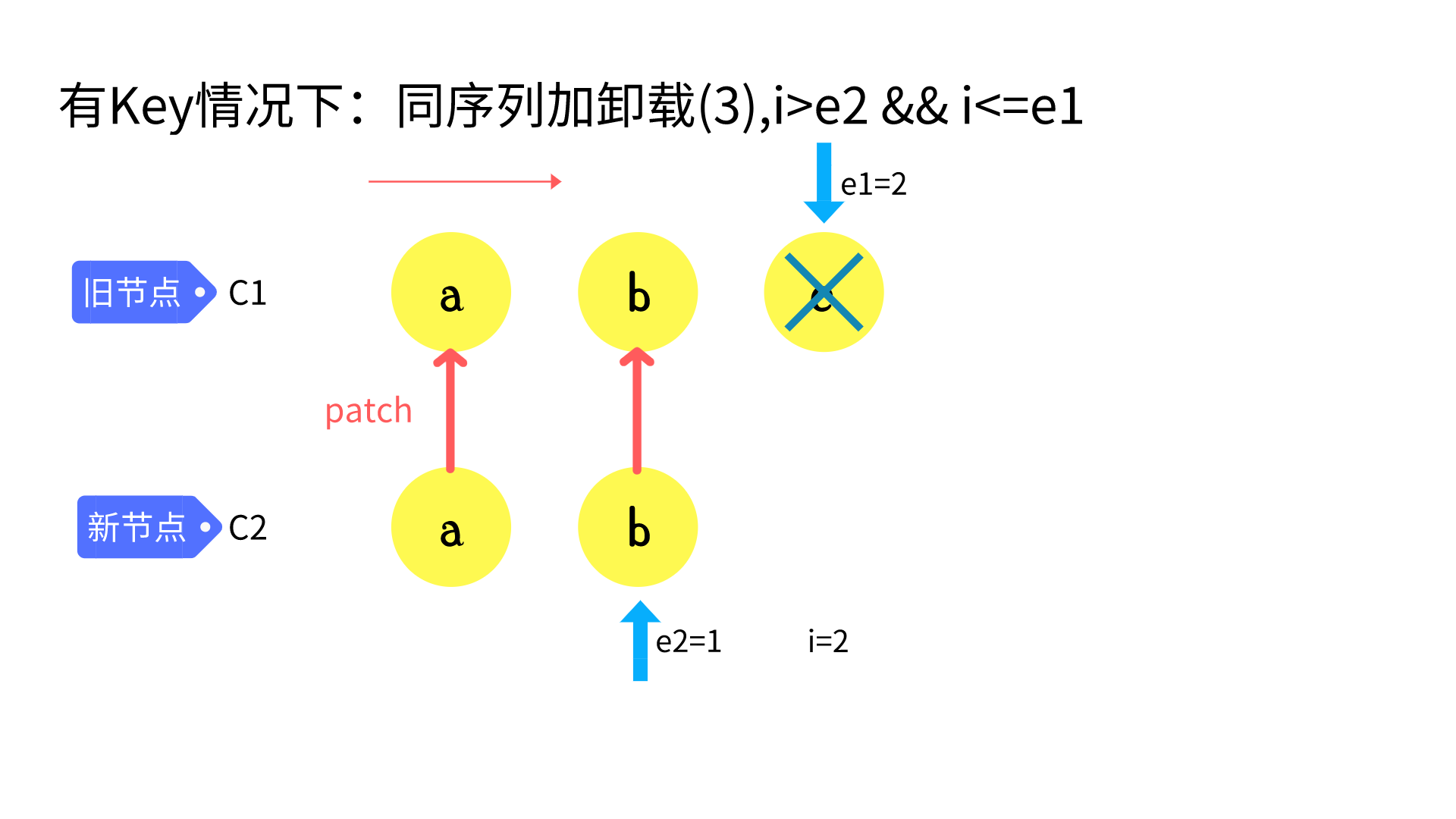
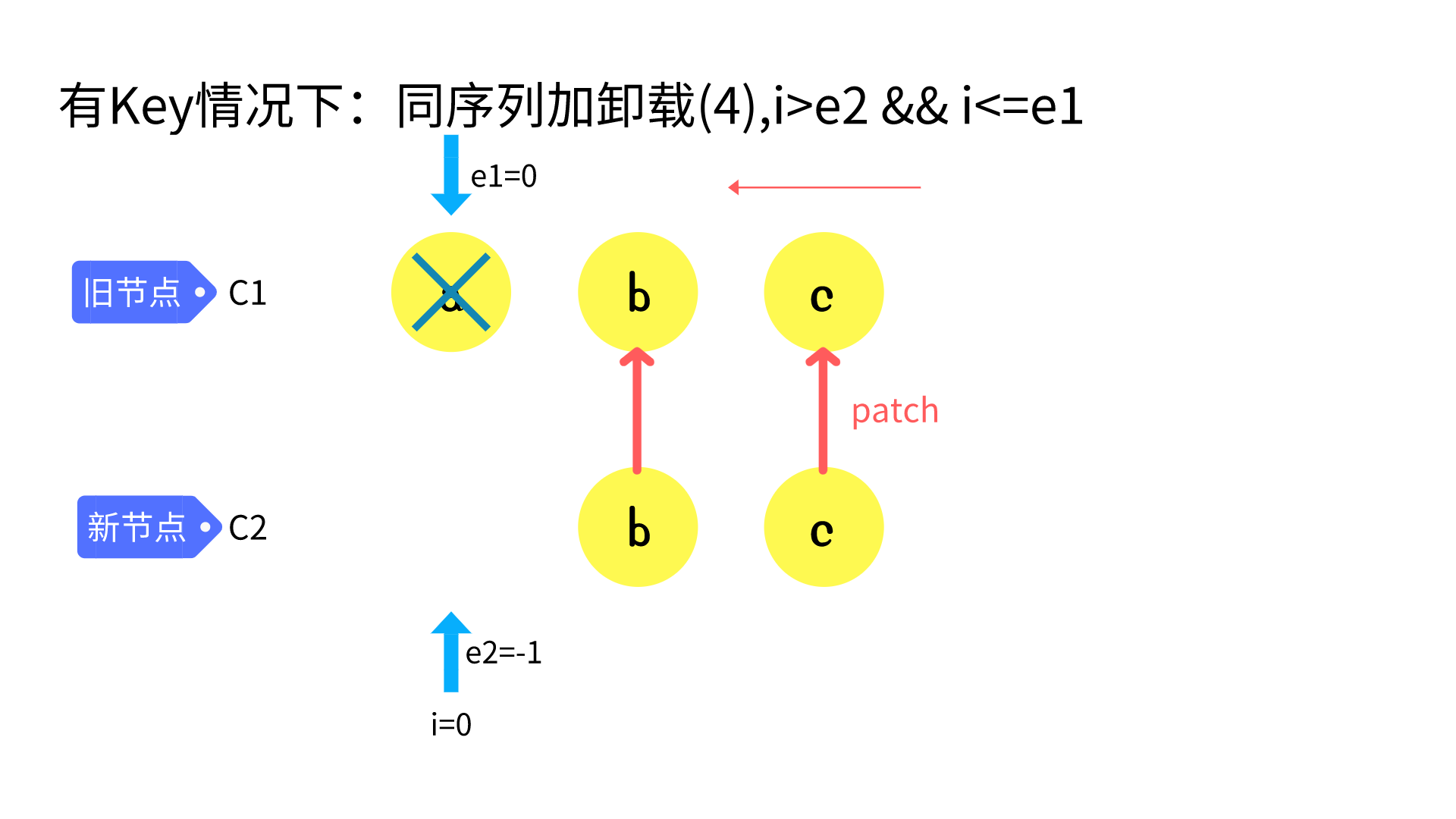
// 4. common sequence + unmount
// (a b) c
// (a b)
// i = 2, e1 = 2, e2 = 1
// a (b c)
// (b c)
// i = 0, e1 = 0, e2 = -1
else if (i > e2) {
while (i <= e1) {
unmount(c1[i])
i++
}
}
unknown sequence
build key:index map for newChildren
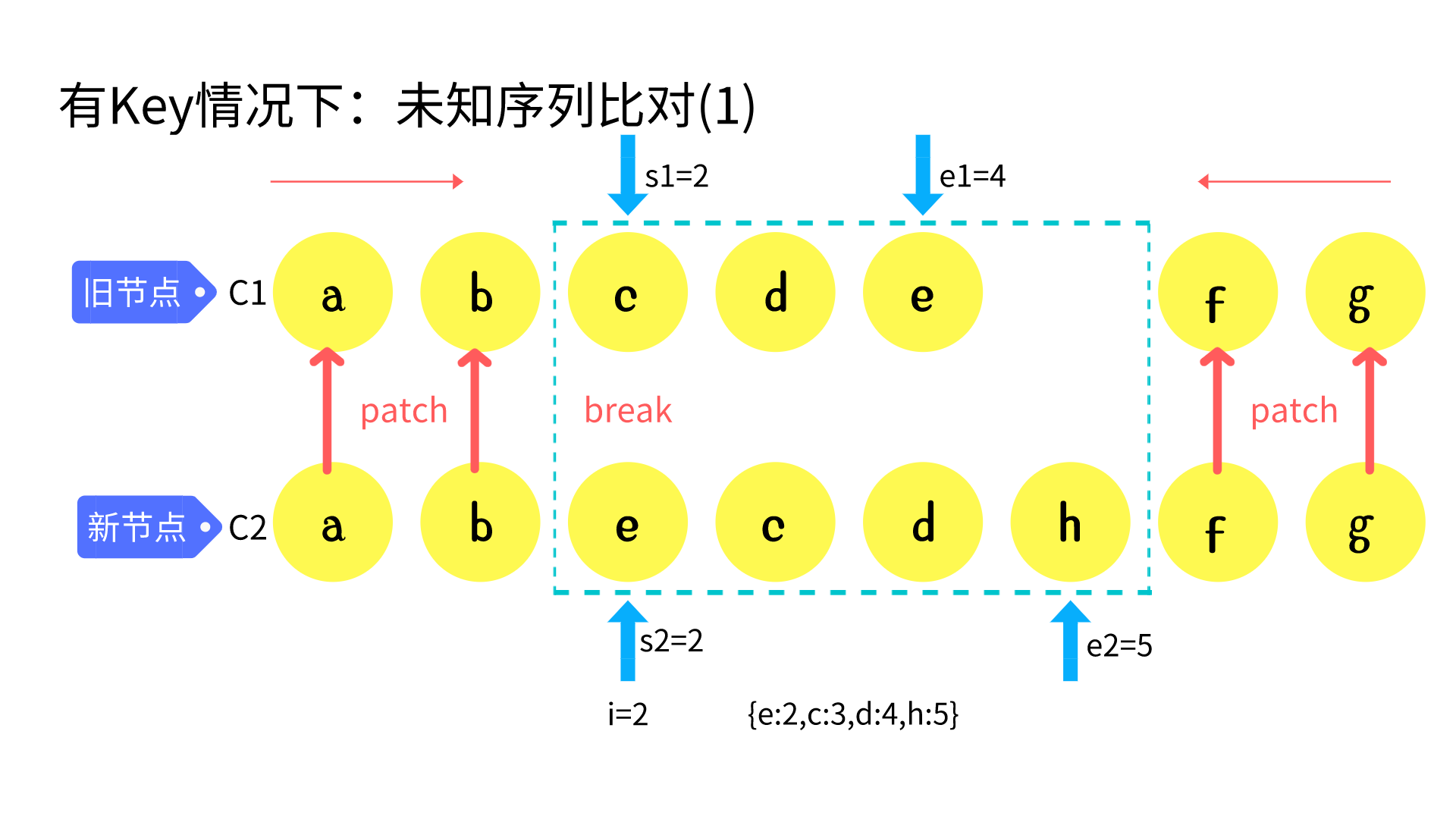
// 5. unknown sequence
// a b [c d e] f g
// a b [e c d h] f g
// i = 2, e1 = 4, e2 = 5
else {
const s1 = i;
const s2 = i;
const keyToNewIndexMap = new Map();
for (let i = s2; i <= e2; i++) {
const nextChild = c2[i];
keyToNewIndexMap.set(nextChild.key, i);
}
}
loop through old children left to be patched and try to patch
// 标记新元素的,对应老元素的索引位置
const toBePatched = e2 - s2 + 1;
const newIndexToOldMapIndex = new Array(toBePatched).fill(0); //
for (let i = s1; i <= e1; i++) {
const prevChild = c1[i];
let newIndex = keyToNewIndexMap.get(prevChild.key); // 获取新的索引
if (newIndex == undefined) {
unmount(prevChild); // 老的有 新的没有直接删除
} else {
newIndexToOldMapIndex[newIndex - s2] = i + 1;
patch(prevChild, c2[newIndex], container);
}
}
move and mount
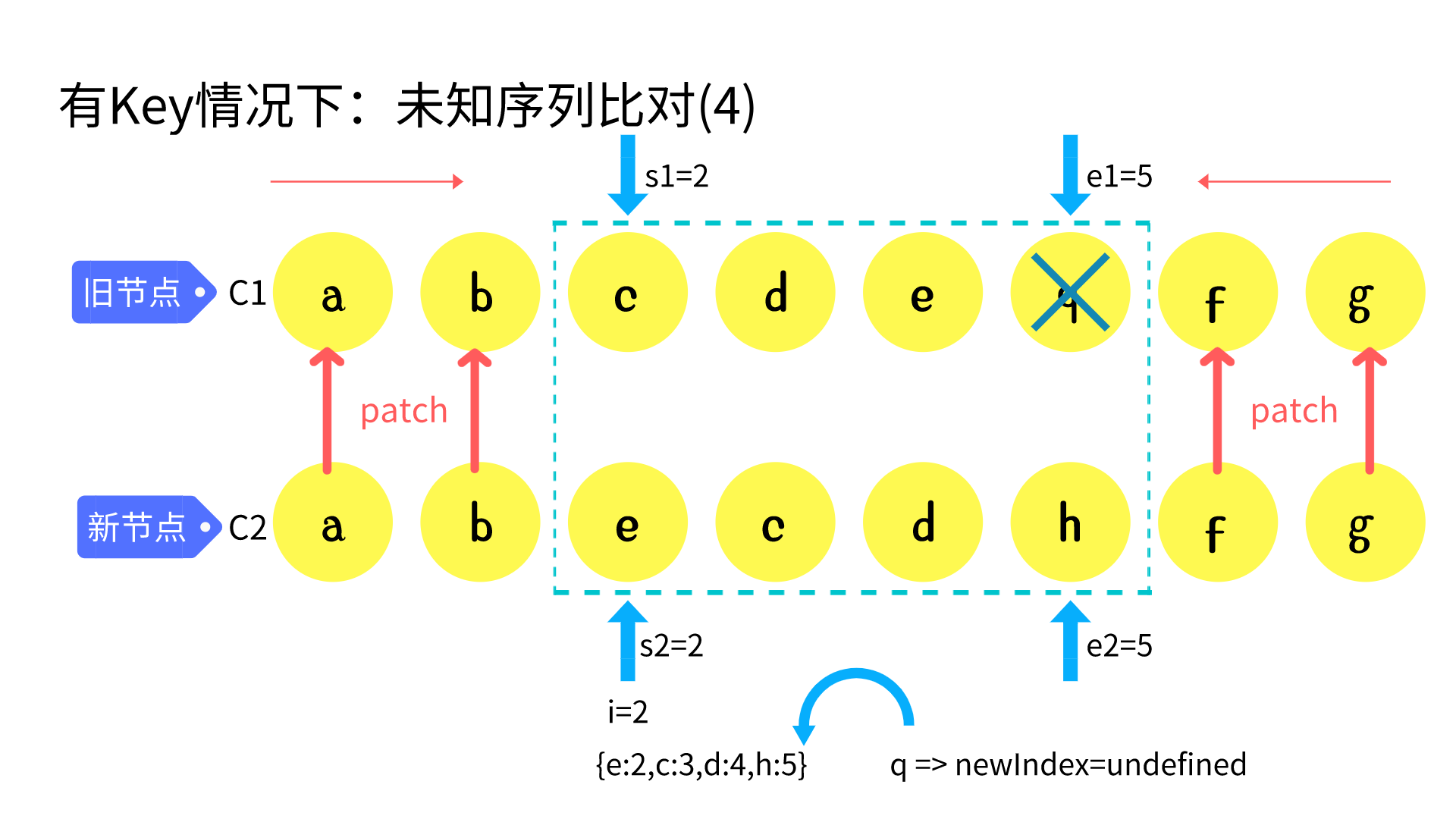
console.log(newIndexToOldMapIndex); // -> 将结果映射成 [1,2] 倒序的时候遇到索引为2和1的跳过操作
for (let i = toBePatched - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
const nextIndex = s2 + i; // [ecdh] 找到h的索引
const nextChild = c2[nextIndex]; // 找到 h
let anchor = nextIndex + 1 < c2.length ? c2[nextIndex + 1].el : null; // 找到当前元素的下一个元素
if (newIndexToOldMapIndex[i] == 0) {
// 这是一个新元素 直接创建插入到 当前元素的下一个即可
patch(null, nextChild, container, anchor);
} else {
// 根据参照物 将节点直接移动过去 所有节点都要移动 (但是有些节点可以不动)
hostInsert(nextChild.el, container, anchor);
}
}
最长递增子序列
最优情况
Vue3 采用最长递增子序列,求解不需要移动的元素有哪些
function getSequence(arr) {
const len = arr.length;
const result = [0]; // 保存最长递增子序列的索引
let resultLastIndex;
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
const arrI = arr[i]; // 获取数组中的每一项,但是0 没有意义我们需要忽略掉
if (arrI !== 0) {
resultLastIndex = result[result.length - 1];
if (arr[resultLastIndex] < arrI) {
result.push(i); // 记录索引
continue;
}
}
}
return result;
}
// 针对默认递增的序列进行优化
console.log(getSequence([2, 6, 7, 8, 9, 11]));
二分查找查找最长递增个数
function getSequence1(arr) {
const len = arr.length;
const result = [0]; // 保存最长递增子序列的索引
let resultLastIndex;
let start;
let end;
let middle = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
const arrI = arr[i]; // 获取数组中的每一项,但是0 没有意义我们需要忽略掉
if (arrI !== 0) {
resultLastIndex = result[result.length - 1];
if (arr[resultLastIndex] < arrI) {
result.push(i); // 记录索引
continue;
}
start = 0;
end = result.length - 1; // 二分查找 前后索引
while (start < end) {
// 最终start = end
middle = ((start + end) / 2) | 0; // 向下取整
// 拿result中间值和最后一项比较
if (arr[result[middle]] < arrI) {
// 找比arrI大的值 或者等于arrI
start = middle + 1;
} else {
end = middle;
}
}
if (arrI < arr[result[start]]) {
// 当前这个小就替换掉
result[start] = i;
}
}
}
return result;
}
前驱节点追溯
假设有:[2,3,1,5,6,8,7,9,4] 为最新序列 -> 按照上述结果得出的结论为:[ 2, 1, 8, 4, 6, 7 ]
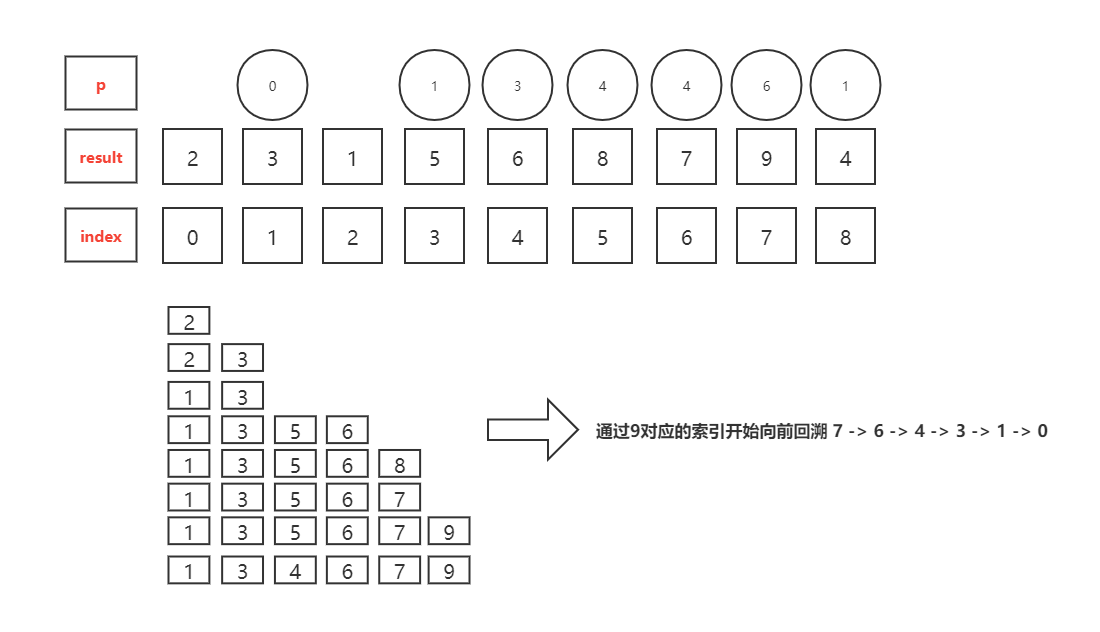
function getSequence(arr) {
// 最终的结果是索引
const len = arr.length;
const result = [0]; // 索引 递增的序列 用二分查找性能高
const p = arr.slice(0); // 里面内容无所谓 和 原本的数组相同 用来存放索引
let start;
let end;
let middle;
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
// O(n)
const arrI = arr[i];
if (arrI !== 0) {
let resultLastIndex = result[result.length - 1];
// 取到索引对应的值
if (arr[resultLastIndex] < arrI) {
p[i] = resultLastIndex; // 标记当前前一个对应的索引
result.push(i);
// 当前的值 比上一个人大 ,直接push ,并且让这个人得记录他的前一个
continue;
}
// 二分查找 找到比当前值大的那一个
start = 0;
end = result.length - 1;
while (start < end) {
// 重合就说明找到了 对应的值 // O(logn)
middle = ((start + end) / 2) | 0; // 找到中间位置的前一个
if (arr[result[middle]] < arrI) {
start = middle + 1;
} else {
end = middle;
} // 找到结果集中,比当前这一项大的数
}
// start / end 就是找到的位置
if (arrI < arr[result[start]]) {
// 如果相同 或者 比当前的还大就不换了
if (start > 0) {
// 才需要替换
p[i] = result[start - 1]; // 要将他替换的前一个记住
}
result[start] = i;
}
}
}
let i = result.length; // 总长度
let last = result[i - 1]; // 找到了最后一项
while (i-- > 0) {
// 根据前驱节点一个个向前查找
result[i] = last; // 最后一项肯定是正确的
last = p[last];
}
return result;
}
console.log(getSequence([2, 3, 1, 5, 6, 8, 7, 9, 4]));
优化Diff算法
利用最长递增子序列,优化Diff算法
// [5,3,4,0] => [1,2]
let increasingNewIndexSequence = getSequence(newIndexToOldMapIndex);
let j = increasingNewIndexSequence.length - 1; // 取出最后一个人的索引
for (let i = toBePatched - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
let currentIndex = i + s2; // 找到h的索引
let child = c2[currentIndex]; // 找到h对应的节点
let anchor = currentIndex + 1 < c2.length ? c2[currentIndex + 1].el : null; // 第一次插入h 后 h是一个虚拟节点,同时插入后 虚拟节点会
if (newIndexToOldMapIndex[i] == 0) {
// 如果自己是0说明没有被patch过
patch(null, child, container, anchor);
} else {
if (i != increasingNewIndexSequence[j]) {
hostInsert(child.el, container, anchor); // 操作当前的d 以d下一个作为参照物插入
} else {
j--; // 跳过不需要移动的元素, 为了减少移动操作 需要这个最长递增子序列算法
}
}
}