1.高阶函数 #
高阶函数(Higher-order functions)是一个在JavaScript中非常重要且强大的概念。它们允许我们编写更简洁、更灵活和更易维护的代码。
在JavaScript中,函数是一等公民(first-class citizens),这意味着我们可以将函数作为变量存储、将它们作为参数传递给其他函数,或者从其他函数返回它们。高阶函数就是利用这一特性,接受一个或多个函数作为参数,或返回一个函数的函数。
1. 高阶函数接受一个或多个函数作为参数
常见的高阶函数包括 map、filter 和 reduce。这些高阶函数都接受一个函数作为参数,并对数组的每个元素应用这个函数。
例如,map 函数将一个函数应用于数组中的每个元素,并返回一个新数组:
const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const doubled = numbers.map(num => num * 2);
console.log(doubled); // [2, 4, 6, 8, 10]
filter 函数接受一个函数作为参数,并返回一个包含那些使该函数返回真值的元素的新数组:
const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const evens = numbers.filter(num => num % 2 === 0);
console.log(evens); // [2, 4]
2. 高阶函数可以返回一个函数
返回函数的高阶函数允许我们创建具有特定行为的新函数。这是函数式编程中的一个常见模式,被称为函数柯里化(currying)或部分应用(partial application)。
例如,下面是一个简单的高阶函数,它接受一个乘数,并返回一个新的函数,该函数将其输入乘以该乘数:
function multiplier(factor) {
return function (x) {
return x * factor;
}
}
const timesTwo = multiplier(2);
console.log(timesTwo(5)); // 10
高阶函数的使用可以使代码更加抽象、更具可重用性,使我们能够将逻辑分解为更小、更容易理解的部分。在JavaScript和其他支持函数式编程的语言中,高阶函数是一个非常有用的工具。
2.函数柯里化 #
函数柯里化(Function Currying)是函数式编程中的一个技术,它可以将接受多个参数的函数转换为一系列使用一个参数的函数。柯里化的主要目的是创建可以轻易地为常见任务进行参数化的函数版本。
为什么要使用柯里化?
- 参数重用:通过固定一部分参数,我们可以创建具有少量参数的新函数。
- 延迟计算:能够创建并返回函数,直到我们得到所有参数后再进行实际的计算。
- 提高可读性和可维护性:使代码更简洁、更具描述性。
如何实现柯里化?
考虑一个简单的两数相加函数:
function add(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
柯里化版本:
function curriedAdd(a) {
return function(b) {
return a + b;
}
}
const add5 = curriedAdd(5);
console.log(add5(3)); // 输出 8
这个例子展示了基本的柯里化,但如果我们想柯里化一个接受多个参数的函数呢?
通用的柯里化函数:
function curry(fn) {
return function curried(...args) {
if (args.length >= fn.length) {
return fn.apply(this, args);
} else {
return function (...args2) {
return curried.apply(this, args.concat(args2));
}
}
};
}
使用上面的 curry 函数,我们可以将任何函数柯里化:
const curriedAdd = curry(add);
console.log(curriedAdd(5)(3)); // 输出 8
注意事项:
- 由于柯里化依赖于闭包,如果你不小心可能会引入意外的副作用或内存泄漏。
- 柯里化可以提高代码的抽象级别,但它也可能降低代码的可读性,特别是对不熟悉函数柯里化的开发者来说。
3.异步编程 #
在 JavaScript 中,异步编程是一种常见的编程范式,特别是在 I/O 密集型任务(如文件读写或网络请求)中。Node.js 提供了非阻塞的 I/O 操作,这意味着主线程不会等待 I/O 操作完成,而是继续执行后续代码。当 I/O 操作完成时,会执行相应的回调函数。
示例:使用 fs.readFile 读取文件 #
Node.js 的 fs 模块提供了 readFile 方法,该方法用于异步读取文件内容。它接受文件路径和回调函数作为参数。
const fs = require('fs');
fs.readFile('path/to/file.txt', 'utf8', (err, data) => {
if (err) {
console.error('Error reading the file:', err);
return;
}
console.log('File content:', data);
});
console.log('Reading file...');
上述代码中,fs.readFile 是一个异步操作。当调用它时,主线程不会等待文件读取完成,而是继续执行 console.log('Reading file...')。一旦文件读取完成,提供给 readFile 的回调函数会被调用。
为什么使用异步编程? #
- 性能:异步操作允许程序继续执行其他任务,而不是被阻塞,等待长时间的操作完成。
- 响应性:在 Web 服务器或用户界面中,这可以确保快速响应,不会因为一个任务而冻结整个系统。
异步编程的挑战 #
尽管异步编程有很多好处,但它也带来了一些挑战:
- 回调地狱(Callback Hell):多个嵌套回调会导致代码难以阅读和维护。这通常被称为“回调地狱”或“金字塔死亡”。
doSomething(result => {
doSomethingElse(result, newResult => {
doYetAnotherThing(newResult, finalResult => {
// ... and so on ...
});
});
});
- 错误处理:传统的
try/catch错误处理在异步回调中不起作用。你必须依赖回调函数的err参数来捕获和处理错误。
为了解决这些挑战,现代 JavaScript 引入了 Promises、async/await 等特性,使异步编程更加直观和易于管理。但回调仍然是 Node.js 和许多库中的常见模式,因此了解其工作原理是很有用的。
4. Promise #
- promisesaplus
- promisesaplus.com.cn
- Promise 是 ES6(ECMAScript 2015)中引入的一种异步编程的解决方案,用于处理异步操作
2.1 创建一个 Promise #
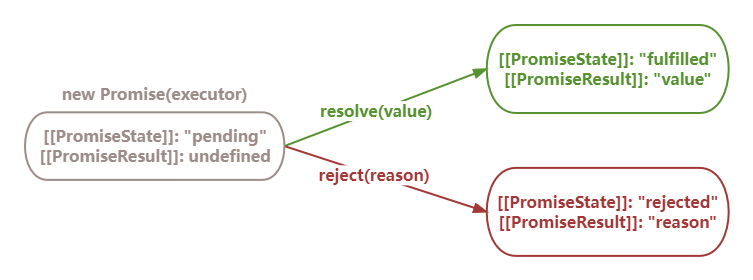
- Promise 是一个表示未来某个将要发生的事件的对象
- 它有三种状态:pending(进行中)、fulfilled(已成功)和rejected(已失败)
- 一个 Promise 对象是通过构造函数 Promise 创建的,接受一个参数:一个包含 resolve 和 reject 两个参数的函数(通常称为“执行器函数”)
- resolve 函数用于将 Promise 状态改变为 fulfilled,reject 函数用于将 Promise 状态改变为 rejected
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
//resolve('value');
//reject('reason');
});
console.dir(promise);
2.2 实例方法 #
| 属性/方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
then |
返回一个新的Promise,并处理Promise的完成(resolved)状态。 |
catch |
返回一个新的Promise,并处理Promise的拒绝(rejected)状态。 |
finally |
返回一个新的Promise,在Promise完成或拒绝后执行一段代码。 |
2.2.1 then #
- Promise对象的then方法接受两个可选参数,分别是onFulfilled和onRejected。这两个参数都是回调函数
- onFulfilled:当Promise状态变为完成(resolved)时执行的回调函数。这个回调函数接收一个参数,即Promise的结果值
- onRejected:当Promise状态变为拒绝(rejected)时执行的回调函数。这个回调函数接收一个参数,即Promise的拒绝原因
2.2.1.1 then #
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
if (Math.random() > 0.5) {
resolve('成功');
} else {
reject('失败');
}
}, 1000);
});
promise.then(
(result) => {
console.log(result);
},
(reason) => {
console.error(reason);
}
);
Promise.js
const PENDING = 'PENDING';
const FULFILLED = 'FULFILLED';
const REJECTED = 'REJECTED';
class Promise {
constructor(executor) {
this.status = PENDING;
this.value = undefined;
this.reason = undefined;
this.onResolvedCallbacks = [];
this.onRejectedCallbacks = [];
const resolve = (value) => {
if (this.status === PENDING) {
this.value = value;
this.status = FULFILLED;
this.onResolvedCallbacks.forEach(fn=>fn());
}
}
const reject = (reason) => {
if (this.status === PENDING) {
this.reason = reason;
this.status = REJECTED;
this.onRejectedCallbacks.forEach(fn=>fn());
}
}
try{
executor(resolve,reject);
}catch(error){
reject(error);
}
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
if(this.status === FULFILLED){
onFulfilled(this.value);
}
if(this.status === REJECTED){
onRejected(this.reason);
}
if(this.status === PENDING){
this.onResolvedCallbacks.push(()=>{
onFulfilled(this.value);
});
this.onRejectedCallbacks.push(()=>{
onRejected(this.reason);
});
}
}
}
module.exports = Promise;
2.2.1.2 可选参数 #
- 2.2.1 onFulfilled和onRejected都是可选参数
- 2.2.1.1 如果onFulfilled不是一个函数,它必须被忽略
- 2.2.1.2 如果onRejected不是一个函数,它必须被忽略
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve('成功');
reject('失败')
});
promise.then().then().then((result) => {
console.log(result);
},(reason) => {
console.error(reason);
});
Promise.js
const PENDING = 'PENDING';
const FULFILLED = 'FULFILLED';
const REJECTED = 'REJECTED';
class Promise {
constructor(executor) {
this.status = PENDING;
this.value = undefined;
this.reason = undefined;
this.onResolvedCallbacks = [];
this.onRejectedCallbacks = [];
const resolve = (value) => {
if (this.status === PENDING) {
this.value = value;
this.status = FULFILLED;
this.onResolvedCallbacks.forEach(fn => fn());
}
}
const reject = (reason) => {
if (this.status === PENDING) {
this.reason = reason;
this.status = REJECTED;
this.onRejectedCallbacks.forEach(fn => fn());
}
}
try {
executor(resolve, reject);
} catch (error) {
reject(error);
}
}
+ then(onFulfilled = value => value, onRejected = reason => { throw reason }) {
+ let promise2 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
+ if (this.status === FULFILLED) {
+ try {
+ const x = onFulfilled(this.value);
+ resolve(x);
+ } catch (error) {
+ reject(error)
+ }
+ }
+ if (this.status === REJECTED) {
+ try {
+ const x = onRejected(this.reason);
+ resolve(x);
+ } catch (error) {
+ reject(error)
+ }
+ }
+ if (this.status === PENDING) {
+ this.onResolvedCallbacks.push(() => {
+ try {
+ const x = onFulfilled(this.value);
+ resolve(x);
+ } catch (error) {
+ reject(error)
+ }
+ });
+ this.onRejectedCallbacks.push(() => {
+ try {
+ const x = onRejected(this.reason);
+ resolve(x);
+ } catch (error) {
+ reject(error)
+ }
+ });
+ }
+ })
+ return promise2;
}
}
module.exports = Promise;
2.2.1.3 onFulfilled #
- 2.2.2 如果onFulfilled是一个函数:
- 2.2.2.1 它必须在promise实现后调用,并以promise的值作为其第一个参数。
- 2.2.2.2 在promise实现之前不得调用它。
- 2.2.2.3 它不能被调用多次
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve('成功');
resolve('成功');
});
promise.then((value) => {
console.log(value);
});
2.2.1.4 onRejected #
- 2.2.3 如果onRejected是一个函数:
- 2.2.3.1 它必须在promise被拒绝后调用,并以promise的原因作为其第一个参数
- 2.2.3.2 在promise被拒绝之前不得调用它
- 2.2.3.3 它不能被调用多次
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
reject('失败');
reject('失败');
});
promise.then(undefined, (error) => {
console.log(error);
});
2.2.1.5 异步 #
- 2.2.4 onFulfilled或onRejected不能在执行上下文堆栈中只包含平台代码之前调用
const Promise = require('./Promise');
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve('成功');
});
promise.then((value) => {
console.log(value);
});
console.log('用户代码执行完毕');
Promise.js
const PENDING = 'PENDING';
const FULFILLED = 'FULFILLED';
const REJECTED = 'REJECTED';
class Promise {
constructor(executor) {
this.status = PENDING;
this.value = undefined;
this.reason = undefined;
this.onResolvedCallbacks = [];
this.onRejectedCallbacks = [];
const resolve = (value) => {
if (this.status === PENDING) {
this.value = value;
this.status = FULFILLED;
this.onResolvedCallbacks.forEach(fn => fn());
}
}
const reject = (reason) => {
if (this.status === PENDING) {
this.reason = reason;
this.status = REJECTED;
this.onRejectedCallbacks.forEach(fn => fn());
}
}
try {
executor(resolve, reject);
} catch (error) {
reject(error);
}
}
then(onFulfilled = value => value, onRejected = reason => { throw reason }) {
let promise2 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if (this.status === FULFILLED) {
+ queueMicrotask(() => {
try {
const x = onFulfilled(this.value);
resolve(x);
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
+ });
}
if (this.status === REJECTED) {
+ queueMicrotask(() => {
try {
const x = onRejected(this.reason);
resolve(x);
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
+ });
}
if (this.status === PENDING) {
this.onResolvedCallbacks.push(() => {
+ queueMicrotask(() => {
try {
const x = onFulfilled(this.value);
resolve(x);
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
+ });
});
this.onRejectedCallbacks.push(() => {
+ queueMicrotask(() => {
try {
const x = onRejected(this.reason);
resolve(x);
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
+ });
});
}
})
return promise2;
}
}
module.exports = Promise;
2.2.1.6 函数调用 #
- 2.2.5 onFulfilled和onRejected必须作为函数被调用(即没有this值)
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve('成功');
});
promise.then(function (value) {
console.log(this);
});
2.2.1.7 多次调用 #
- 2.2.6 then方法可以在同一个promise上多次调用
- 2.2.6.1 如果/当promise被实现时,所有相应的onFulfilled回调函数必须按照它们发起then调用的顺序执行
- 2.2.6.2 如果/当promise被拒绝时,所有相应的onRejected回调函数必须按照它们发起then调用的顺序执行
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve('成功');
});
promise.then(function (value) {
console.log(1, value);
});
promise.then(function (value) {
console.log(2, value);
});
2.2.1.8 返回promise #
- 2.2.7 then方法必须返回一个promise
- 2.2.7.1 promise2 = promise1.then(onFulfilled, onRejected)
- 2.2.7.2 如果onFulfilled或onRejected返回一个值x,则运行Promise Resolution Procedure [Resolve]
- 2.2.7.3 如果onFulfilled或onRejected抛出异常e,则promise2必须以e作为原因被拒绝
- 2.2.7.4 如果onFulfilled不是一个函数且promise1被实现,则promise2必须以与promise1相同的值被实现
- 2.2.7.5 如果onRejected不是一个函数且promise1被拒绝,则promise2必须以与promise1相同的原因被拒绝
2.2.7.3
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve('成功');
});
let promise2 = promise.then(function (value) {
console.log(value);
throw new Error('then error');
});
promise2.then(undefined, function (err) {
console.log(err);
});
2.2.7.4 2.2.7.5
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
//resolve('成功');
reject('失败');
});
let promise2 = promise.then();
promise2.then(function (value) {
console.log(value);
}, function (err) {
console.log(err);
});
2.2.1.9 Promise Resolution Procedure #
- [Resolve]
- 2.3.1 如果promise和x引用同一个对象,则以TypeError为原因拒绝promise
//const Promise = require('./Promise');
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve('成功');
});
let promise2 = promise.then(function (value) {
return promise2;
});
promise2.then(
(value) => { console.log(value) },
(reason) => { console.log(reason) });
Promise.js
const PENDING = 'PENDING';
const FULFILLED = 'FULFILLED';
const REJECTED = 'REJECTED';
+function resolvePromise(x, promise2, resolve, reject) {
+ if (x === promise2) {
+ return reject(new TypeError('Chaining cycle detected for promise #<Promise>'))
+ }
+}
class Promise {
constructor(executor) {
this.status = PENDING;
this.value = undefined;
this.reason = undefined;
this.onResolvedCallbacks = [];
this.onRejectedCallbacks = [];
const resolve = (value) => {
if (this.status === PENDING) {
this.value = value;
this.status = FULFILLED;
this.onResolvedCallbacks.forEach(fn => fn());
}
}
const reject = (reason) => {
if (this.status === PENDING) {
this.reason = reason;
this.status = REJECTED;
this.onRejectedCallbacks.forEach(fn => fn());
}
}
try {
executor(resolve, reject);
} catch (error) {
reject(error);
}
}
then(onFulfilled = value => value, onRejected = reason => { throw reason }) {
let promise2 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if (this.status === FULFILLED) {
queueMicrotask(() => {
try {
const x = onFulfilled(this.value);
+ resolvePromise(x, promise2, resolve, reject)
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
});
}
if (this.status === REJECTED) {
queueMicrotask(() => {
try {
const x = onRejected(this.reason);
+ resolvePromise(x, promise2, resolve, reject)
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
});
}
if (this.status === PENDING) {
this.onResolvedCallbacks.push(() => {
queueMicrotask(() => {
try {
const x = onFulfilled(this.value);
+ resolvePromise(x, promise2, resolve, reject)
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
});
});
this.onRejectedCallbacks.push(() => {
queueMicrotask(() => {
try {
const x = onRejected(this.reason);
+ resolvePromise(x, promise2, resolve, reject)
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
});
});
}
})
return promise2;
}
}
module.exports = Promise;
- 2.3.1 如果x是一个promise,采用其状态
- 2.3.1.1 如果x处于待定状态,则promise必须保持待定状态,直到x被实现或拒绝
- 2.3.1.2 如果/当x被实现时,用相同的值实现promise
- 2.3.1.3 如果/当x被拒绝时,用相同的原因拒绝promise
const Promise = require('./Promise');
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve('成功');
});
let promise2 = promise.then(function (value) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve('success');
//reject('error');
});;
});
promise2.then(function (value) {
console.log(value);
}, function (reason) {
console.log(reason);
}
);
Promise.js
const PENDING = 'PENDING';
const FULFILLED = 'FULFILLED';
const REJECTED = 'REJECTED';
function resolvePromise(x, promise2, resolve, reject) {
if (x === promise2) {
return reject(new TypeError('Chaining cycle detected for promise #<Promise>'))
}
+ if ((typeof x === 'object' && x !== null) || (typeof x === 'function')) {
+ let then = x.then;
+ if (typeof then === 'function') {
+ then.call(x, y => {
+ resolvePromise(y, promise2, resolve, reject)
+ }, r => {
+ reject(r);
+ });
+ } else {
+ resolve(x);
+ }
+ } else {
+ resolve(x);
+ }
}
class Promise {
constructor(executor) {
this.status = PENDING;
this.value = undefined;
this.reason = undefined;
this.onResolvedCallbacks = [];
this.onRejectedCallbacks = [];
const resolve = (value) => {
if (this.status === PENDING) {
this.value = value;
this.status = FULFILLED;
this.onResolvedCallbacks.forEach(fn => fn());
}
}
const reject = (reason) => {
if (this.status === PENDING) {
this.reason = reason;
this.status = REJECTED;
this.onRejectedCallbacks.forEach(fn => fn());
}
}
try {
executor(resolve, reject);
} catch (error) {
reject(error);
}
}
then(onFulfilled = value => value, onRejected = reason => { throw reason }) {
let promise2 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if (this.status === FULFILLED) {
queueMicrotask(() => {
try {
const x = onFulfilled(this.value);
resolvePromise(x, promise2, resolve, reject)
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
});
}
if (this.status === REJECTED) {
queueMicrotask(() => {
try {
const x = onRejected(this.reason);
resolvePromise(x, promise2, resolve, reject)
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
});
}
if (this.status === PENDING) {
this.onResolvedCallbacks.push(() => {
queueMicrotask(() => {
try {
const x = onFulfilled(this.value);
resolvePromise(x, promise2, resolve, reject)
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
});
});
this.onRejectedCallbacks.push(() => {
queueMicrotask(() => {
try {
const x = onRejected(this.reason);
resolvePromise(x, promise2, resolve, reject)
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
});
});
}
})
return promise2;
}
}
module.exports = Promise;
- 2.3.3 否则,如果x是一个对象或函数:
- 2.3.3.1 让then为x.then
- 2.3.3.2 如果获取属性x .then导致抛出异常e,则以e为原因拒绝promise
const Promise = require('./Promise');
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve('成功');
});
let promise2 = promise.then(function (value) {
let obj = {};
Object.defineProperty(obj, 'then', {
get() {
throw new Error();
}
});
return obj;
});
promise2.then(function (value) {
console.log(value);
}, function (reason) {
console.log(reason);
}
);
Promise.js
const PENDING = 'PENDING';
const FULFILLED = 'FULFILLED';
const REJECTED = 'REJECTED';
function resolvePromise(x, promise2, resolve, reject) {
if (x === promise2) {
return reject(new TypeError('Chaining cycle detected for promise #<Promise>'))
}
if ((typeof x === 'object' && x !== null) || (typeof x === 'function')) {
+ try {
let then = x.then;
if (typeof then === 'function') {
then.call(x, y => {
resolvePromise(y, promise2, resolve, reject)
}, r => {
reject(r);
});
} else {
resolve(x);
}
+ }catch(error){
+ reject(error);
+ }
} else {
resolve(x);
}
}
class Promise {
constructor(executor) {
this.status = PENDING;
this.value = undefined;
this.reason = undefined;
this.onResolvedCallbacks = [];
this.onRejectedCallbacks = [];
const resolve = (value) => {
if (this.status === PENDING) {
this.value = value;
this.status = FULFILLED;
this.onResolvedCallbacks.forEach(fn => fn());
}
}
const reject = (reason) => {
if (this.status === PENDING) {
this.reason = reason;
this.status = REJECTED;
this.onRejectedCallbacks.forEach(fn => fn());
}
}
try {
executor(resolve, reject);
} catch (error) {
reject(error);
}
}
then(onFulfilled = value => value, onRejected = reason => { throw reason }) {
let promise2 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if (this.status === FULFILLED) {
queueMicrotask(() => {
try {
const x = onFulfilled(this.value);
resolvePromise(x, promise2, resolve, reject)
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
});
}
if (this.status === REJECTED) {
queueMicrotask(() => {
try {
const x = onRejected(this.reason);
resolvePromise(x, promise2, resolve, reject)
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
});
}
if (this.status === PENDING) {
this.onResolvedCallbacks.push(() => {
queueMicrotask(() => {
try {
const x = onFulfilled(this.value);
resolvePromise(x, promise2, resolve, reject)
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
});
});
this.onRejectedCallbacks.push(() => {
queueMicrotask(() => {
try {
const x = onRejected(this.reason);
resolvePromise(x, promise2, resolve, reject)
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
});
});
}
})
return promise2;
}
}
module.exports = Promise;
- 2.3.3.3 如果then是一个函数,则以x作为this,第一个参数为resolvePromise,第二个参数为rejectPromise调用它,其中:
- 2.3.3.3.1 如果当resolvePromise被调用并传入值y,运行[Resolve]
- 2.3.3.3.2 如果当rejectPromise被调用并传入原因r,以r拒绝promise
- 2.3.3.3.3 如果resolvePromise和rejectPromise都被调用,或者对同一个参数进行多次调用,则第一次调用优先,任何后续调用都将被忽略
- 2.3.3.3.4 如果调用then导致抛出异常e,
- 2.3.3.3.4.1 如果已经调用了resolvePromise或rejectPromise,则忽略它
- 2.3.3.3.4.1 否则,以e为原因拒绝promise
const Promise = require('./Promise');
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve('成功');
});
let promise2 = promise.then(function (value) {
let obj = {
then(resolvePromise, rejectPromise) {
//resolvePromise('成功2');
rejectPromise('失败2');
throw new Error('失败3');
}
};
return obj;
});
promise2.then(function (value) {
console.log(value);
},function (reason) {
console.log(reason);
});
const PENDING = 'PENDING';
const FULFILLED = 'FULFILLED';
const REJECTED = 'REJECTED';
function resolvePromise(x, promise2, resolve, reject) {
if (x === promise2) {
return reject(new TypeError('Chaining cycle detected for promise #<Promise>'))
}
if ((typeof x === 'object' && x !== null) || (typeof x === 'function')) {
+ let called = false
try {
let then = x.then;
if (typeof then === 'function') {
then.call(x, y => {
+ if (called) return
+ called = true
resolvePromise(y, promise2, resolve, reject)
}, r => {
+ if (called) return
+ called = true
reject(r);
});
} else {
resolve(x);
}
}catch(error){
+ if (called) return
+ called = true
reject(error);
}
} else {
resolve(x);
}
}
class Promise {
constructor(executor) {
this.status = PENDING;
this.value = undefined;
this.reason = undefined;
this.onResolvedCallbacks = [];
this.onRejectedCallbacks = [];
const resolve = (value) => {
if (this.status === PENDING) {
this.value = value;
this.status = FULFILLED;
this.onResolvedCallbacks.forEach(fn => fn());
}
}
const reject = (reason) => {
if (this.status === PENDING) {
this.reason = reason;
this.status = REJECTED;
this.onRejectedCallbacks.forEach(fn => fn());
}
}
try {
executor(resolve, reject);
} catch (error) {
reject(error);
}
}
then(onFulfilled = value => value, onRejected = reason => { throw reason }) {
let promise2 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if (this.status === FULFILLED) {
queueMicrotask(() => {
try {
const x = onFulfilled(this.value);
resolvePromise(x, promise2, resolve, reject)
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
});
}
if (this.status === REJECTED) {
queueMicrotask(() => {
try {
const x = onRejected(this.reason);
resolvePromise(x, promise2, resolve, reject)
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
});
}
if (this.status === PENDING) {
this.onResolvedCallbacks.push(() => {
queueMicrotask(() => {
try {
const x = onFulfilled(this.value);
resolvePromise(x, promise2, resolve, reject)
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
});
});
this.onRejectedCallbacks.push(() => {
queueMicrotask(() => {
try {
const x = onRejected(this.reason);
resolvePromise(x, promise2, resolve, reject)
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
});
});
}
})
return promise2;
}
}
module.exports = Promise;
- 2.3.3.4 如果then不是一个函数,则以x来实现promise
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve('成功');
});
let promise2 = promise.then(function (value) {
let obj = { name: 'zhufeng' };
Object.defineProperty(obj, 'then', {
get() {
return 'then string'
}
});
return obj;
});
promise2.then(function (value) {
console.log(value);
}, function (reason) {
console.log(reason);
}
);
- 2.3.4 如果x不是对象或函数,则用x来实现promise
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve('成功');
});
let promise2 = promise.then(function (value) {
return [1, 2, 3];
});
promise2.then(function (value) {
console.log(value);
}, function (reason) {
console.log(reason);
}
);
2.2.2 catch #
- Promise对象的catch方法用于捕获和处理Promise的拒绝(rejected)状态
- 它是then方法的一种特殊形式,专门用于处理拒绝状态,而不处理完成(resolved)状态
- catch方法接受一个回调函数作为参数,该回调函数会在Promise被拒绝时被调用,并接收拒绝的原因作为参数
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
reject('出错了');
}, 1000);
});
promise.catch((reason) => {
console.error(reason);
});
+ catch(onRejected) {
+ return this.then(undefined, onRejected);
+ }
2.2.3 finally #
- Promise对象的finally方法是一个用于指定无论Promise状态如何都会执行的回调函数。它在Promise链中的最后一个位置,不管Promise是完成(resolved)还是拒绝(rejected),finally方法都会被调用
- finally方法接受一个回调函数作为参数,该回调函数没有任何参数,它仅在Promise状态变为完成或拒绝时被调用
const Promise = require('./Promise');
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
//resolve('成功');
reject('reason');
});
promise
.finally(() => {
console.log('无论如何都会执行');
});
finally(callback) {
return this.then(
value => new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
queueMicrotask(() => {
try {
callback();
resolve(value);
} catch (error) {
reject(error);
}
});
}),
reason => new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
queueMicrotask(() => {
try {
callback();
reject(reason);
} catch (error) {
reject(error);
}
});
})
);
}
2.2.4 链式调用 #
- then 方法可以被多次调用,每次调用都会返回一个新的 Promise 对象。这样就可以通过链式调用的方式,依次处理多个异步操作的结果
const Promise = require('./Promise');
const fs = require('fs');
function readFileAsync(path) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
fs.readFile(path, 'utf8', (err, data) => {
if (err) reject(err);
else resolve(data);
});
});
}
readFileAsync("name.txt")
.then(nameData => {
console.log(nameData);
return readFileAsync("age.txt");
})
.then(ageData => {
console.log(ageData);
})
.catch(error => {
console.error("An error occurred:", error);
});
2.3 静态方法 #
| 静态方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| Promise.all | 返回一个 Promise,该 Promise 在所有给定的 Promise 都已解决时解决,并且返回所有 Promise 的解决值数组,顺序与传入的 Promise 数组顺序一致。如果传入的任何 Promise 被拒绝,则返回的 Promise 将立即被拒绝,并且会传递拒绝的原因。 |
| Promise.race | 返回一个 Promise,该 Promise 在给定的 Promise 数组中的任何一个 Promise 解决或拒绝时解决或拒绝。返回的 Promise 采用第一个解决或拒绝的 Promise 的值或原因。 |
| Promise.resolve | 返回一个已解决的 Promise 对象,解析结果由传入的值决定。如果传入的是一个 Promise 对象,则返回该对象本身。如果传入的是一个 thenable 对象(即具有 then 方法的对象),则返回的 Promise 将采用该 thenable 对象的状态。否则,返回的 Promise 将以传入的值为解决值。 |
| Promise.reject | 返回一个拒绝的 Promise 对象,拒绝原因由传入的值决定。 |
| Promise.allSettled | 返回一个 Promise,该 Promise 在所有给定的 Promise 都已解决或拒绝后解决,并返回一个包含所有 Promise 结果的数组,每个结果是一个对象,包含该 Promise 的状态和值或原因。 |
| Promise.any | 返回一个 Promise,该 Promise 在给定的 Promise 数组中的任何一个 Promise 解决时解决。如果所有 Promise 都被拒绝,则返回的 Promise 将被拒绝,并且会传递所有 Promise 的拒绝原因数组。 |
2.3.1 Promise.resolve #
- Promise.resolve 是 Promise 的一个静态方法,用于创建一个已解决(resolved)的 Promise 对象
- 它可以接收一个值作为参数,并返回一个以该值为解决值的 Promise 对象
- Promise.resolve 方法返回一个新的 Promise 对象,具有以下行为:
- 如果 value 是一个 Promise 对象,返回的 Promise 对象将与 value 相同
- 如果 value 是一个 thenable 对象(即具有 then 方法的对象),返回的 Promise 对象将采用该 thenable 对象的状态
- 如果 value 是一个普通的非 Promise、非 thenable 对象,返回的 Promise 对象将以 value 作为解决值
- 如果 value 未指定任何值,返回的 Promise 对象将立即解决,并且解决值为 undefined
Promise.resolve(value);
Promise.resolve('Hello')
.then(value => {
console.log(value); // 'Hello'
return 42;
})
Promise.js
+static resolve(value) {
+ return new Promise((resolve) => {
+ resolve(value);
+ });
+}
2.3.2 Promise.reject #
- Promise.reject 是 Promise 的一个静态方法,用于创建一个已拒绝(rejected)的 Promise 对象
- 它可以接收一个拒绝原因作为参数,并返回一个以该原因为拒绝原因的 Promise 对象
Promise.reject(reason);
Promise.reject(new Error('Something went wrong'))
.catch(error => {
console.error(error.message); // 'Something went wrong'
});
Promise.js
+ static reject(reason) {
+ return new Promise((_, reject) => {
+ reject(reason);
+ });
+ }
2.3.3 Promise.all #
- Promise.all 是 Promise 的一个静态方法。它接收一个可迭代对象(如数组或类数组对象)作为参数,并返回一个新的 Promise
- 这个 Promise 在传入的可迭代对象中的所有 Promise 都成功解决时才会被解决,否则只要有一个 Promise 被拒绝,返回的 Promise 就会立即被拒绝
- iterable:一个可迭代对象,包含多个 Promise 对象
- Promise.all 方法返回一个新的 Promise 对象,它将根据以下规则解决或拒绝:
- 如果 iterable 是空数组,Promise.all 会立即解决,返回一个空数组作为解决值
- 如果 iterable 中的所有 Promise 都解决(即成功解决),则返回的 Promise 会以一个数组作为解决值。这个数组包含了传入的可迭代对象中所有 Promise 解决的值,顺序与可迭代对象中的顺序一致
- 如果 iterable 中的任何一个 Promise 被拒绝,返回的 Promise 会立即被拒绝,并传递被拒绝的 Promise 的原因作为拒绝原因
Promise.all(iterable);
const promise1 = Promise.resolve('Hello');
const promise2 = 42;
const promise3 = new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(resolve, 1000, 'World');
});
Promise.all([promise1, promise2, promise3])
.then(values => {
console.log(values); // ['Hello', 42, 'World']
})
.catch(error => {
console.error(error);
});
Promise.js
const resolve = (value) => {
+ if (value instanceof Promise) {
+ return value.then(resolve, reject)
+ }
if (this.status === PENDING) {
this.value = value;
this.status = FULFILLED;
this.onResolvedCallbacks.forEach(fn => fn());
}
}
+ static all(promises) {
+ return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
+ let results = [];
+ let completed = 0;
+ promises.forEach((promise, index) => {
+ Promise.resolve(promise).then(value => {
+ results[index] = value;
+ completed++;
+ if (completed === promises.length) {
+ resolve(results);
+ }
+ }, reason => {
+ reject(reason);
+ });
+ });
+ });
+ }
2.3.4 Promise.race #
- Promise.race 是 Promise 的一个静态方法,用于创建一个新的 Promise 对象,该 Promise 对象将与传入的多个 Promise 对象竞争(race)解决或拒绝。它接收一个可迭代对象(如数组或类数组对象)作为参数,并返回一个新的 Promise
- Promise.race 方法返回一个新的 Promise 对象,具有以下行为:
- 返回的 Promise 对象将采用第一个解决或拒绝的 Promise 的值或原因
- 当传入的多个 Promise 对象中有一个解决或拒绝时,返回的 Promise 对象将与该解决或拒绝的 Promise 对象的状态一致
- 如果传入的可迭代对象为空,则返回的 Promise 将永远等待,不会被解决或拒绝。
通过 Promise.race 方法,可以同时启动多个异步操作,并使用最先解决或拒绝的 Promise 的结果进行后续处理
iterable:一个可迭代对象,包含多个 Promise 对象
Promise.race(iterable);
const promise1 = new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, 1000, 'Promise 1 resolved'));
const promise2 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => setTimeout(reject, 500, 'Promise 2 rejected'));
const promise3 = new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, 1500, 'Promise 3 resolved'));
Promise.race([promise1, promise2, promise3])
.then(result => {
console.log(result); // 'Promise 2 rejected'
})
.catch(error => {
console.error(error); // 'Promise 2 rejected'
});
Proimse.js
+ static race(promises) {
+ return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
+ promises.forEach(promise => {
+ Promise.resolve(promise).then(value => {
+ resolve(value);
+ }, reason => {
+ reject(reason);
+ });
+ });
+ });
+ }
2.3.6 Promise.any #
- Promise.any 是 Promise 的一个静态方法,用于创建一个新的 Promise 对象,该 Promise 对象在传入的多个 Promise 对象中至少有一个解决时就解决。它接收一个可迭代对象(如数组或类数组对象)作为参数,并返回一个新的 Promise
- Promise.any 方法返回一个新的 Promise 对象,具有以下行为:
- 返回的 Promise 对象将采用第一个解决的 Promise 的值
- 当传入的多个 Promise 对象中有一个解决时,返回的 Promise 对象将与该解决的 Promise 对象的状态一致
- 如果传入的所有 Promise 都被拒绝,返回的 Promise 对象将被拒绝,并传递所有 Promise 的拒绝原因数组
通过 Promise.any 方法,可以同时启动多个异步操作,并使用最快解决的 Promise 的结果进行后续处理
iterable:一个可迭代对象,包含多个 Promise 对象
Promise.any(iterable);
const promise1 = new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, 2000, 'Promise 1 resolved'));
const promise2 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => setTimeout(reject, 1000, 'Promise 2 rejected'));
const promise3 = new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, 1500, 'Promise 3 resolved'));
Promise.any([promise1, promise2, promise3])
.then(result => {
console.log(result); // 'Promise 3 resolved'
})
.catch(errors => {
console.error(errors); // [AggregateError: All promises were rejected]
});
Promise.js
+ static any(promises) {
+ return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
+ let completed = 0;
+ let reasons = [];
+ promises.forEach((promise, index) => {
+ Promise.resolve(promise).then(value => {
+ resolve(value);
+ }, reason => {
+ reasons[index] = reason;
+ completed++;
+ if (completed === promises.length) {
+ reject(new AggregateError(reasons, "All promises were rejected"));
+ }
+ });
+ });
+ });
+ }
2.3.5 Promise.allSettled #
- Promise.allSettled 是 Promise 的一个静态方法,用于创建一个新的 Promise 对象,该 Promise 对象在传入的多个 Promise 对象全部解决或拒绝后解决,并返回一个包含所有 Promise 结果的数组,每个结果是一个对象,包含该 Promise 的状态和值或原因
- Promise.allSettled 方法返回一个新的 Promise 对象,具有以下行为:
- 返回的 Promise 对象将在传入的所有 Promise 对象都解决或拒绝后解决
- 返回的 Promise 对象将解决为一个数组,该数组包含了传入的可迭代对象中每个 Promise 的结果对象。每个结果对象都包含以下两个属性:
- status:表示 Promise 的状态,可能的取值为 'fulfilled'(解决)或 'rejected'(拒绝)
- value(仅当状态为 'fulfilled' 时存在):表示 Promise 的解决值
- reason(仅当状态为 'rejected' 时存在):表示 Promise 的拒绝原因
- 通过 Promise.allSettled 方法,可以同时启动多个异步操作,并等待它们全部完成后获取所有的结果,不论是解决还是拒绝
Promise.allSettled(iterable);
const promise1 = Promise.resolve('Resolved');
const promise2 = Promise.reject('Rejected');
const promise3 = new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, 1000, 'Delayed Resolved'));
Promise.allSettled([promise1, promise2, promise3])
.then(results => {
console.log(results);
/* [
{ status: 'fulfilled', value: 'Resolved' },
{ status: 'rejected', reason: 'Rejected' },
{ status: 'fulfilled', value: 'Delayed Resolved' }
] */
});
Promise.js
+ static allSettled(promises) {
+ return new Promise(resolve => {
+ let results = [];
+ let completed = 0;
+ promises.forEach((promise, index) => {
+ Promise.resolve(promise).then(value => {
+ results[index] = { status: 'fulfilled', value };
+ completed++;
+ if (completed === promises.length) {
+ resolve(results);
+ }
+ }, reason => {
+ results[index] = { status: 'rejected', reason };
+ completed++;
+ if (completed === promises.length) {
+ resolve(results);
+ }
+ });
+ });
+ });
+ }