- 1. typescript是什么
- 2. TypeScript安装和编译
- 3. 数据类型
- 4. 函数
- 5. 类
- 6. 接口
- 7. 泛型
- 8.结构类型系统
- 9.类型保护
- 10. 类型变换
1. typescript是什么 #
- Typescript是由微软开发的一款开源的编程语言
- Typescript是Javascript的超集,遵循最新的ES5/ES6规范。TypeScript扩展了Javascript语法
- TypeScript更像后端Java、C#这样的面向对象语言可以让JS开发大型企业应用
- 越来越多的项目是基于TS的,比如VSCode、Angular6、Vue3、React16
- TS提供的类型系统可以帮助我们在写代码的时候提供更丰富的语法提示
- 在创建前的编译阶段经过类型系统的检查,就可以避免很多线上的错误
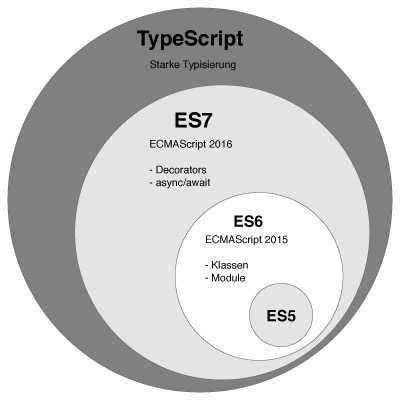
2. TypeScript安装和编译 #
2.1 安装 #
cnpm i typescript -g
tsc helloworld.ts
2.2 Vscode+TypeScript #
2.2.1 生成配置文件 #
tsc --init
{
"compilerOptions": {
/* Basic Options */
"target": "es5", /* Specify ECMAScript target version: 'ES3' (default), 'ES5', 'ES2015', 'ES2016', 'ES2017','ES2018' or 'ESNEXT'. 指定ECMAScript的目标版本*/
"module": "commonjs", /* Specify module code generation: 'none', 'commonjs', 'amd', 'system', 'umd', 'es2015', or 'ESNext'. 指定模块代码的生成方式*/
// "lib": [], /* Specify library files to be included in the compilation. 指定编译的时候用来包含的编译文件*/
// "allowJs": true, /* Allow javascript files to be compiled. 允许编译JS文件*/
// "checkJs": true, /* Report errors in .js files. 在JS中包括错误*/
// "jsx": "preserve", /* Specify JSX code generation: 'preserve', 'react-native', or 'react'. 指定JSX代码的生成方式 是保留还是react-native或者react*/
// "declaration": true, /* Generates corresponding '.d.ts' file.生成相应的类型声明文件 */
// "declarationMap": true, /* Generates a sourcemap for each corresponding '.d.ts' file. 为每个类型声明文件生成相应的sourcemap*/
// "sourceMap": true, /* Generates corresponding '.map' file. 生成对应的map文件 */
// "outFile": "./", /* Concatenate and emit output to single file. 合并并且把编译后的内容输出 到一个文件里*/
// "outDir": "./", /* Redirect output structure to the directory.按原始结构输出到目标目录 */
// "rootDir": "./", /* Specify the root directory of input files. Use to control the output directory structure with --outDir. 指定输入文件的根目录,用--outDir来控制输出的目录结构*/
// "composite": true, /* Enable project compilation 启用项目编译*/
// "removeComments": true, /* Do not emit comments to output. 移除注释*/
// "noEmit": true, /* Do not emit outputs. 不要输出*/
// "importHelpers": true, /* Import emit helpers from 'tslib'. */
// "downlevelIteration": true, /* Provide full support for iterables in 'for-of', spread, and destructuring when targeting 'ES5' or 'ES3'. 当目标是ES5或ES3的时候提供对for-of、扩展运算符和解构赋值中对于迭代器的完整支持*/
// "isolatedModules": true, /* Transpile each file as a separate module (similar to 'ts.transpileModule').r把每一个文件转译成一个单独的模块 */
/* Strict Type-Checking Options */
//"strict": true, /* Enable all strict type-checking options. 启用完全的严格类型检查 */
// "noImplicitAny": true, /* Raise error on expressions and declarations with an implied 'any' type. 不能使用隐式的any类型*/
// "strictNullChecks": true, /* Enable strict null checks. 启用严格的NULL检查*/
// "strictFunctionTypes": true, /* Enable strict checking of function types. 启用严格的函数类型检查*/
// "strictBindCallApply": true, /* Enable strict 'bind', 'call', and 'apply' methods on functions.启用函数上严格的bind call 和apply方法 */
// "strictPropertyInitialization": true, /* Enable strict checking of property initialization in classes. 启用类上初始化属性检查*/
// "noImplicitThis": true, /* Raise error on 'this' expressions with an implied 'any' type.在默认的any中调用 this表达式报错 */
// "alwaysStrict": true, /* Parse in strict mode and emit "use strict" for each source file. 在严格模式下解析并且向每个源文件中发射use strict*/
/* Additional Checks */
// "noUnusedLocals": true, /* Report errors on unused locals. 有未使用到的本地变量时报错 */
// "noUnusedParameters": true, /* Report errors on unused parameters. 有未使用到的参数时报错*/
// "noImplicitReturns": true, /* Report error when not all code paths in function return a value. 当不是所有的代码路径都有返回值的时候报错*/
// "noFallthroughCasesInSwitch": true, /* Report errors for fallthrough cases in switch statement. 在switch表达式中没有替代的case会报错 */
/* Module Resolution Options */
// "moduleResolution": "node", /* Specify module resolution strategy: 'node' (Node.js) or 'classic' (TypeScript pre-1.6). 指定模块的解析策略 node classic*/
// "baseUrl": "./", /* Base directory to resolve non-absolute module names. 在解析非绝对路径模块名的时候的基准路径*/
// "paths": {}, /* A series of entries which re-map imports to lookup locations relative to the 'baseUrl'. 一些路径的集合*/
// "rootDirs": [], /* List of root folders whose combined content represents the structure of the project at runtime. 根目录的列表,在运行时用来合并内容*/
// "typeRoots": [], /* List of folders to include type definitions from. 用来包含类型声明的文件夹列表*/
// "types": [], /* Type declaration files to be included in compilation.在编译的时候被包含的类型声明 */
// "allowSyntheticDefaultImports": true, /* Allow default imports from modules with no default export. This does not affect code emit, just typechecking.当没有默认导出的时候允许默认导入,这个在代码执行的时候没有作用,只是在类型检查的时候生效 */
//"esModuleInterop": true /* Enables emit interoperability between CommonJS and ES Modules via creation of namespace objects for all imports. Implies 'allowSyntheticDefaultImports'.*/
// "preserveSymlinks": true, /* Do not resolve the real path of symlinks.不要symlinks解析的真正路径 */
/* Source Map Options */
// "sourceRoot": "", /* Specify the location where debugger should locate TypeScript files instead of source locations. 指定ts文件位置*/
// "mapRoot": "", /* Specify the location where debugger should locate map files instead of generated locations. 指定 map文件存放的位置 */
// "inlineSourceMap": true, /* Emit a single file with source maps instead of having a separate file. 源文件和sourcemap 文件在同一文件中,而不是把map文件放在一个单独的文件里*/
// "inlineSources": true, /* Emit the source alongside the sourcemaps within a single file; requires '--inlineSourceMap' or '--sourceMap' to be set. 源文件和sourcemap 文件在同一文件中*/
/* Experimental Options */
// "experimentalDecorators": true, /* Enables experimental support for ES7 decorators. 启动装饰器*/
// "emitDecoratorMetadata": true, /* Enables experimental support for emitting type metadata for decorators. */
}
}
2.2.2 执行编译 #
tsc
2.2.3 vscode运行 #
- Terminal->Run Task-> tsc:build 编译
- Terminal->Run Task-> tsc:watch 编译并监听
2.2.4 npm scripts #
- npm run 实际上是调用本地的 Shell 来执行对应的 script value,所以理论上能兼容所有 bash 命令
- Shell 在类 Unix 系统上是 /bin/sh,在 Windows 上是 cmd.exe
2.2.5 npm scripts 的 PATH #
- npm run 会预置 PATH,对应包下的 node_modules/.bin 目录
3. 数据类型 #
3.1 布尔类型(boolean) #
let married: boolean=false;
3.2 数字类型(number) #
let age: number=10;
3.3 字符串类型(string) #
let firstname: string='zfpx';
3.4 数组类型(array) #
let arr2: number[]=[4,5,6];
let arr3: Array<number>=[7,8,9];
3.5 元组类型(tuple) #
- 在 TypeScript 的基础类型中,元组( Tuple )表示一个已知
数量和类型的数组
let zhufeng:[string,number] = ['zhufeng',5];
zhufeng[0].length;
zhufeng[1].toFixed(2);
| 元组 | 数组 |
|---|---|
| 每一项可以是不同的类型 | 每一项都是同一种类型 |
| 有预定义的长度 | 没有长度限制 |
| 用于表示一个结构 | 用于表示一个列表 |
const animal:[string,number,boolean] = ['zhufeng',10,true];
3.6 枚举类型(enum) #
- 事先考虑某一个变量的所有的可能的值,尽量用自然语言中的单词表示它的每一个值
- 比如性别、月份、星期、颜色、单位、学历
3.6.1 普通枚举 #
enum Gender{
GIRL,
BOY
}
console.log(`李雷是${Gender.BOY}`);
console.log(`韩梅梅是${Gender.GIRL}`);
enum Week{
MONDAY=1,
TUESDAY=2
}
console.log(`今天是星期${Week.MONDAY}`);
3.6.2 常数枚举 #
- 常数枚举与普通枚举的区别是,它会在编译阶段被删除,并且不能包含计算成员。
- 假如包含了计算成员,则会在编译阶段报错
const enum Colors {
Red,
Yellow,
Blue
}
let myColors = [Colors.Red, Colors.Yellow, Colors.Blue];
const enum Color {Red, Yellow, Blue = "blue".length};
3.7 任意类型(any) #
any就是可以赋值给任意类型- 第三方库没有提供类型文件时可以使用
any - 类型转换遇到困难时
- 数据结构太复杂难以定义
let root:any=document.getElementById('root');
root.style.color='red';
3.8 null 和 undefined #
- null 和 undefined 是其它类型的子类型,可以赋值给其它类型,如数字类型,此时,赋值后的类型会变成 null 或 undefined
- strictNullChecks
let x: number;
x = 1;
x = undefined;
x = null;
let y: number | null | undefined;
y = 1;
y = undefined;
y = null;
3.9 void 类型 #
- void 表示没有任何类型
- 当一个函数没有返回值时,TS 会认为它的返回值是 void 类型。
- 当我们声明一个变量类型是 void 的时候,它的非严格模式下仅可以被赋值为 null 和 undefined;
function greeting(name:string):void {
console.log('hello',name);
}
greeting('zfpx');
3.10 never类型 #
never是其它类型(null undefined)的子类型,代表不会出现的值
3.10.1 #
- 作为不会返回( return )的函数的返回值类型
// 返回never的函数 必须存在 无法达到( unreachable ) 的终点
function error(message: string): never {
throw new Error(message);
}
// 由类型推论得到返回值为 never
function fail() {
return error("Something failed");
}
// 返回never的函数 必须存在 无法达到( unreachable ) 的终点
function infiniteLoop(): never {
while (true) {}
}
3.10.2 strictNullChecks #
- 在 TS 中, null 和 undefined 是任何类型的有效值,所以无法正确地检测它们是否被错误地使用。于是 TS 引入了 --strictNullChecks 这一种检查模式
- 由于引入了 --strictNullChecks ,在这一模式下,null 和 undefined 能被检测到。所以 TS 需要一种新的底部类型( bottom type )。所以就引入了 never。
// Compiled with --strictNullChecks
function fn(x: number | string) {
if (typeof x === 'number') {
// x: number 类型
} else if (typeof x === 'string') {
// x: string 类型
} else {
// x: never 类型
// --strictNullChecks 模式下,这里的代码将不会被执行,x 无法被观察
}
}
3.10.3 never 和 void 的区别 #
- void 可以被赋值为 null 和 undefined的类型。 never 则是一个不包含值的类型。
- 拥有 void 返回值类型的函数能正常运行。拥有 never 返回值类型的函数无法正常返回,无法终止,或会抛出异常。
3.11 类型推论 #
- 是指编程语言中能够自动推导出值的类型的能力,它是一些强静态类型语言中出现的特性
- 定义时未赋值就会推论成any类型
- 如果定义的时候就赋值就能利用到类型推论
let username2;
username2 = 10;
username2 = 'zhufeng';
username2 = null;
3.12 包装对象(Wrapper Object) #
- JavaScript 的类型分为两种:原始数据类型(Primitive data types)和对象类型(Object types)。
- 所有的原始数据类型都没有属性(property)
- 原始数据类型
- 布尔值
- 数值
- 字符串
- null
- undefined
- Symbol
let name = 'zhufeng';
console.log(name.toUpperCase());
console.log((new String('zhufeng')).toUpperCase());
- 当调用基本数据类型方法的时候,JavaScript 会在原始数据类型和对象类型之间做一个迅速的强制性切换
let isOK: boolean = true; // 编译通过
let isOK: boolean = Boolean(1) // 编译通过
let isOK: boolean = new Boolean(1); // 编译失败 期望的 isOK 是一个原始数据类型
3.13 联合类型 #
- 联合类型上只能访问两个类型共有的属性和方法
let name4: string | number;
name4 = 3;
name4 = 'zhufeng';
console.log(name4.toUpperCase());
3.14 类型断言 #
- 类型断言可以将一个联合类型的变量,指定为一个更加具体的类型
- 不能将联合类型断言为不存在的类型
let name5: string | number;
(name5 as number).toFixed(3);
(name5 as string).length;
(name5 as boolean);
3.15 字符串、数字、布尔值字面量 #
type Lucky = 1 | 'One'|true;
let foo:Lucky = 'One';
3.16 字符串字面量 vs 联合类型 #
- 字符串字面量类型用来约束取值只能是某
几个字符串中的一个, 联合类型(Union Types)表示取值可以为多种类型中的一种 - 字符串字面量 限定了使用该字面量的地方仅接受特定的值,联合类型 对于值并没有限定,仅仅限定值的类型需要保持一致
4. 函数 #
4.1 函数的定义 #
function hello(name:string):void {
console.log('hello',name);
}
hello('zfpx');
4.2 函数表达式 #
- 定义函数类型
type GetUsernameFunction = (x:string,y:string)=>string;
let getUsername:GetUsernameFunction = function(firstName,lastName){
return firstName + lastName;
}
4.3 没有返回值 #
let hello2 = function (name:string):void {
console.log('hello2',name);
}
hello('zfpx');
hello2('zfpx');
4.4 可选参数 #
在TS中函数的形参和实参必须一样,不一样就要配置可选参数,而且必须是最后一个参数
function print(name:string,age?:number):void {
console.log(name,age);
}
print('zfpx');
4.5 默认参数 #
function ajax(url:string,method:string='GET') {
console.log(url,method);
}
ajax('/users');
4.6 剩余参数 #
function sum(...numbers:number[]) {
return numbers.reduce((val,item)=>val+=item,0);
}
console.log(sum(1,2,3));
4.7 函数重载 #
- 在Java中的重载,指的是两个或者两个以上的同名函数,参数不一样
- 在TypeScript中,表现为给同一个函数提供多个函数类型定义
let obj: any={};
function attr(val: string): void;
function attr(val: number): void;
function attr(val:any):void {
if (typeof val === 'number') {
obj.age=val;
} else {
obj.name=val;
}
}
attr('zfpx');
attr(9);
attr(true);
console.log(obj);
5. 类 #
5.1 如何定义类 #
class Person{
name:string;
getName():void{
console.log(this.name);
}
}
let p1 = new Person();
p1.name = 'zhufeng';
p1.getName();
5.2 存取器 #
- 在 TypeScript 中,我们可以通过存取器来改变一个类中属性的读取和赋值行为
- 构造函数
- 主要用于初始化类的成员变量属性
- 类的对象创建时自动调用执行
- 没有返回值
class User {
myname:string;
constructor(myname: string) {
this.myname = myname;
}
get name() {
return this.myname;
}
set name(value) {
this.myname = value;
}
}
let user = new User('zhufeng');
user.name = 'jiagou';
console.log(user.name);
5.3 参数属性 #
class User {
constructor(public myname: string) {}
get name() {
return this.myname;
}
set name(value) {
this.myname = value;
}
}
let user = new User('zhufeng');
console.log(user.name);
user.name = 'jiagou';
console.log(user.name);
5.4 readonly #
- readonly修饰的变量只能在
构造函数中初始化 - 在 TypeScript 中,const 是
常量标志符,其值不能被重新分配 - TypeScript 的类型系统同样也允许将 interface、type、 class 上的属性标识为 readonly
- readonly 实际上只是在
编译阶段进行代码检查。而 const 则会在运行时检查(在支持 const 语法的 JavaScript 运行时环境中)
class Animal {
public readonly name: string
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
}
changeName(name:string){
this.name = name;
}
}
let a = new Animal('zhufeng');
a.changeName('jiagou');
5.5 继承 #
- 子类继承父类后子类的实例就拥有了父类中的属性和方法,可以增强代码的可复用性
- 将子类公用的方法抽象出来放在父类中,自己的特殊逻辑放在子类中重写父类的逻辑
- super可以调用父类上的方法和属性
class Person {
name: string;//定义实例的属性,默认省略public修饰符
age: number;
constructor(name:string,age:number) {//构造函数
this.name=name;
this.age=age;
}
getName():string {
return this.name;
}
setName(name:string): void{
this.name=name;
}
}
class Student extends Person{
no: number;
constructor(name:string,age:number,no:number) {
super(name,age);
this.no=no;
}
getNo():number {
return this.no;
}
}
let s1=new Student('zfpx',10,1);
console.log(s1);
5.6 类里面的修饰符 #
class Father {
public name: string; //类里面 子类 其它任何地方外边都可以访问
protected age: number; //类里面 子类 都可以访问,其它任何地方不能访问
private money: number; //类里面可以访问, 子类和其它任何地方都不可以访问
constructor(name:string,age:number,money:number) {//构造函数
this.name=name;
this.age=age;
this.money=money;
}
getName():string {
return this.name;
}
setName(name:string): void{
this.name=name;
}
}
class Child extends Father{
constructor(name:string,age:number,money:number) {
super(name,age,money);
}
desc() {
console.log(`${this.name} ${this.age} ${this.money}`);
}
}
let child = new Child('zfpx',10,1000);
console.log(child.name);
console.log(child.age);
console.log(child.money);
5.7 静态属性 静态方法 #
class Father {
static className='Father';
static getClassName() {
return Father.className;
}
public name: string;
constructor(name:string) {//构造函数
this.name=name;
}
}
console.log(Father.className);
console.log(Father.getClassName());
5.8 抽象类 #
- 抽象描述一种抽象的概念,无法被实例化,只能被继承
- 无法创建抽象类的实例
- 抽象方法不能在抽象类中实现,只能在抽象类的具体子类中实现,而且必须实现
abstract class Animal3 {
name:string;
abstract speak();
}
class Cat extends Animal3{
speak(){
console.log('喵喵喵');
}
}
let cat = new Cat();
cat.speak();
| 访问控制修饰符 | private protected public |
|---|---|
| 只读属性 | readonly |
| 静态属性 | static |
| 抽象类、抽象方法 | abstract |
5.9 抽象类 vs 接口 #
- 不同类之间公有的属性或方法,可以抽象成一个接口(Interfaces)
- 而抽象类是供其他类继承的基类,抽象类不允许被实例化。抽象类中的抽象方法必须在子类中被实现
- 抽象类本质是一个无法被实例化的类,其中能够实现方法和初始化属性,而接口仅能够用于描述,既不提供方法的实现,也不为属性进行初始化
- 一个类可以继承一个类或抽象类,但可以实现(implements)多个接口
- 抽象类也可以实现接口
abstract class Animal5{
name:string;
constructor(name:string){
this.name = name;
}
abstract speak();
}
interface Flying{
fly()
}
class Duck extends Animal5 implements Flying{
speak(){
console.log('汪汪汪');
}
fly(){
console.log('我会飞');
}
}
let duck = new Duck('zhufeng');
duck.speak();
duck.fly();
5.10 抽象方法 #
- 抽象类和方法不包含具体实现,必须在子类中实现
- 抽象方法只能出现在抽象类中
abstract class Animal{
abstract speak():void;
}
class Dog extends Animal{
speak(){
console.log('小狗汪汪汪');
}
}
class Cat extends Animal{
speak(){
console.log('小猫喵喵喵');
}
}
let dog=new Dog();
let cat=new Cat();
dog.speak();
cat.speak();
5.11 重写(override) vs 重载(overload) #
- 重写是指子类重写继承自父类中的方法
- 重载是指为同一个函数提供多个类型定义
class Cat6 extends Animal6{
speak(word:string):string{
return 'Cat:'+word;
}
}
let cat6 = new Cat6();
console.log(cat6.speak('hello'));
function double(val:number):number
function double(val:string):string
function double(val:any):any{
if(typeof val == 'number'){
return val *2;
}
return val + val;
}
let r = double(1);
console.log(r);
5.12 继承 vs 多态 #
- 继承(Inheritance)子类继承父类,子类除了拥有父类的所有特性外,还有一些更具体的特性
- 多态(Polymorphism)由继承而产生了相关的不同的类,对同一个方法可以有不同的响应
class Animal7{
speak(word:string):string{
return 'Animal: '+word;
}
}
class Cat7 extends Animal7{
speak(word:string):string{
return 'Cat:'+word;
}
}
class Dog7 extends Animal7{
speak(word:string):string{
return 'Dog:'+word;
}
}
let cat7 = new Cat7();
console.log(cat7.speak('hello'));
let dog7 = new Dog7();
console.log(dog7.speak('hello'));
6. 接口 #
- 接口一方面可以在面向对象编程中表示为
行为的抽象,另外可以用来描述对象的形状 - 接口就是把一些类中共有的属性和方法抽象出来,可以用来约束实现此接口的类
- 一个类可以继承另一个类并实现多个接口
- 接口像插件一样是用来增强类的,而抽象类是具体类的抽象概念
- 一个类可以实现多个接口,一个接口也可以被多个类实现,但一个类的可以有多个子类,但只能有一个父类
6.1 接口 #
- interface中可以用分号或者逗号分割每一项,也可以什么都不加
//接口可以用来描述`对象的形状`,少属性或者多属性都会报错
interface Speakable{
speak():void;
name?:string;//?表示可选属性
}
let speakman:Speakable = {
name:string;//多属性也会报错
speak(){}//少属性会报错
}
//接口可以在面向对象编程中表示为行为的抽象
interface Speakable{
speak():void;
}
interface Eatable{
eat():void
}
class Person5 implements Speakable,Eatable{
speak(){
console.log('Person5说话');
}
eat(){}
}
class TangDuck implements Speakable{
speak(){
console.log('TangDuck说话');
}
eat(){}
}
//无法预先知道有哪些新的属性的时候,可以使用 `[propName:string]:any`,propName名字是任意的
interface Person {
readonly id: number;
name: string;
[propName: string]: any;
}
let p1 = {
id:1,
name:'zhufeng',
age:10
}
6.2 接口的继承 #
- 一个接口可以继承自另外一个接口
interface Speakable{
speak():void
}
interface SpeakChinese extends Speakable{
speakChinese():void
}
class Person5 implements SpeakChinese{
speak(){
console.log('Person5')
}
speakChinese(){
console.log('speakChinese')
}
}
6.3 readonly #
- 用 readonly 定义只读属性可以避免由于多人协作或者项目较为复杂等因素造成对象的值被重写
interface Person{
readonly id:number;
name:string
}
let tom:Person = {
id :1,
name:'zhufeng'
}
tom.id = 1;
6.4 函数类型接口 #
- 对方法传入的参数和返回值进行约束
interface discount{
(price:number):number
}
let cost:discount = function(price:number):number{
return price * .8;
}
6.5 可索引接口 #
- 对数组和对象进行约束
- userInterface 表示:只要 index 的类型是 number,那么值的类型必须是 string
- UserInterface2 表示:只要 index 的类型是 string,那么值的类型必须是 string
interface UserInterface {
[index:number]:string
}
let arr:UserInterface = ['zfpx1','zfpx2'];
console.log(arr);
interface UserInterface2 {
[index:string]:string
}
let obj:UserInterface2 = {name:'zhufeng'};
6.6 类接口 #
- 对类的约束
interface Speakable{
name:string;
speak(words:string):void
}
class Dog implements Speakable{
name:string;
speak(words){
console.log(words);
}
}
let dog=new Dog();
dog.speak('汪汪汪');
6.7 构造函数的类型 #
- 在 TypeScript 中,我们可以用 interface 来描述类
- 同时也可以使用interface里特殊的new()关键字来描述类的构造函数类型
class Animal{
constructor(public name:string){
}
}
interface WithNameClass{
new(name:string):Animal
}
function createAnimal(clazz:WithNameClass,name:string){
return new clazz(name);
}
let a = createAnimal(Animal,'zhufeng');
console.log(a.name);
7. 泛型 #
- 泛型(Generics)是指在定义函数、接口或类的时候,不预先指定具体的类型,而在使用的时候再指定类型的一种特性
- 泛型
T作用域只限于函数内部使用
7.1 泛型函数 #
- 首先,我们来实现一个函数 createArray,它可以创建一个指定长度的数组,同时将每一项都填充一个默认值
function createArray(length: number, value: any): Array<any> {
let result: any = [];
for (let i = 0; i < length; i++) {
result[i] = value;
}
return result;
}
let result = createArray(3,'x');
console.log(result);
function createArray(length: number, value: any): Array<any> {
let result: any = [];
for (let i = 0; i < length; i++) {
result[i] = value;
}
return result;
}
let result = createArray(3,'x');
console.log(result);
function createArray2<T>(length: number, value: T): Array<T> {
let result: T[] = [];
for (let i = 0; i < length; i++) {
result[i] = value;
}
return result;
}
let result2 = createArray2<string>(3,'x');
console.log(result);
7.2 类数组 #
- 类数组(Array-like Object)不是数组类型,比如
arguments
function sum(...parameters:number[]){
let args:IArguments = arguments;
for(let i=0;i<args.length;i++){
console.log(args[i]);
}
}
sum(1,2,3);
let root = document.getElementById('root');
let children:HTMLCollection = root.children;
children.length;
let nodeList:NodeList = root.childNodes;
nodeList.length;
7.3 泛型类 #
class MyArray<T>{
private list:T[]=[];
add(value:T) {
this.list.push(value);
}
getMax():T {
let result=this.list[0];
for (let i=0;i<this.list.length;i++){
if (this.list[i]>result) {
result=this.list[i];
}
}
return result;
}
}
let arr=new MyArray();
arr.add(1); arr.add(2); arr.add(3);
let ret = arr.getMax();
console.log(ret);
7.5 泛型接口 #
- 泛型接口可以用来约束函数
interface Calculate{
<T>(a:T,b:T):T
}
let add:Calculate = function<T>(a:T,b:T){
return a;
}
add<number>(1,2);
7.6 多个类型参数 #
- 泛型可以有多个
function swap<A,B>(tuple:[A,B]):[B,A]{
return [tuple[1],tuple[0]];
}
let swapped = swap<string,number>(['a',1]);
console.log(swapped);
console.log(swapped[0].toFixed(2));
console.log(swapped[1].length);
7.7 默认泛型类型 #
function createArray3<T=number>(length: number, value: T): Array<T> {
let result: T[] = [];
for (let i = 0; i < length; i++) {
result[i] = value;
}
return result;
}
let result2 = createArray3(3,'x');
console.log(result2);
7.8 泛型约束 #
- 在函数中使用泛型的时候,由于预先并不知道泛型的类型,所以不能随意访问相应类型的属性或方法。
function logger<T>(val:T){
console.log(val.length)
}
interface LengthWise{
length:number
}
//可以让泛型继承一个接口
function logger2<T extends LengthWise>(val:T){
console.log(val.length)
}
logger2(1);
logger2('zhufeng');
7.9 泛型接口 #
- 定义接口的时候也可以指定泛型
interface Cart<T>{
list:T[]
}
let cart:Cart<{name:string,price:number}> = {
list:[{name:'zhufeng',price:10}]
}
console.log(cart.list[0].name,cart.list[0].price);
7.10 泛型类型别名 #
- 泛型类型别名可以表达更复杂的类型
type Cart<T> = {list:T[]} | T[];
let c1:Cart<string> = {list:['1']};
let c2:Cart<number> = [1];
7.11 泛型接口 vs 泛型类型别名 #
- 接口创建了一个新的名字,它可以在其他任意地方被调用。而类型别名并不创建新的名字,例如报错信息就不会使用别名
- 类型别名不能被 extends和 implements,这时我们应该尽量使用接口代替类型别名
- 当我们需要使用联合类型或者元组类型的时候,类型别名会更合适
8.结构类型系统 #
8.1 接口的兼容性 #
- 如果传入的变量和声明的类型不匹配,TS就会进行兼容性检查
- 原理是
Duck-Check,就是说只要目标类型中声明的属性变量在源类型中都存在就是兼容的
interface Animal{
name:string;
age:number;
gender:number
}
let a1 = {
name:'zhufeng',
age:10,
gender:0
}
interface Person{
name:string;
age:number
}
////- 要判断目标类型`Person`是否能够兼容输入的源类型`Animal`
function getName(p:Person):string{
return p.name;
}
getName(a1);
//只有在传参的时候两个变量之间才会进行兼容性的比较,赋值的时候并不会比较,会直接报错
let x:Person = {
name:'zhufeng',
age:10,
gender:0
}
8.2 基本类型的兼容性 #
//基本数据类型也有兼容性判断
let num : string|number;
let str:string;
num = str;
//只要有toString()方法
let num2 : {
toString():string
}
let str2:string;
num2 = str2;
8.3 类的兼容性 #
- 在TS中是结构类型系统,只会对比结构而不在意类型
class Animal{
name:string
}
class Bird extends Animal{
swing:number
}
let a:Animal;
a = new Bird();
let b:Bird;
//并不是父类兼容子类,子类不兼容父类
b = new Animal();
class Animal{
name:string
}
//如果父类和子类结构一样,也可以的
class Bird extends Animal{}
let a:Animal;
a = new Bird();
let b:Bird;
b = new Animal();
//甚至没有关系的两个类的实例也是可以的
class Animal{
name:string
}
class Bird{
name:string
}
let a:Animal ;
a = new Bird();
let b:Bird;
b = new Animal();
8.4 函数的兼容性 #
- 比较函数的时候是要先比较函数的参数,再比较函数的返回值
- 参数可以省略
type sumFunc = (a:number,b:number)=>number;
let sum:sumFunc;
function f1(a:number,b:number){
return a+b;
}
sum = f1;
//可以省略一个参数
function f2(a:number):number{
return a;
}
sum = f2;
//可以省略二个参数
function f3():number{
return 0;
}
sum = f3;
//多一个参数可不行
function f4(a:number,b:number,c:number){
return a+b+c;
}
sum = f4;
type GetPerson = ()=>{name:string,age:number};
let getPerson:GetPerson;
//参数一样可以
function g1(){
return {name:'zhufeng',age:10};
}
getPerson = g1;
//多一个属性也可以
function g2(){
return {name:'zhufeng',age:10,gender:'male'};
}
getPerson = g2;
//少一个属性不行
function g3(){
return {name:'zhufeng'};
}
getPerson = g3;
//因为有可能要调用返回值上的方法
getPerson().age.toFixed();
8.5 函数参数的双向协变 #
- 函数的参数中目标兼容源,或者源兼容目标都可以,只要有一个成立就可以
type LogFunc = (a:number|string)=>void;
let log:LogFunc;
function log1(a:number){
console.log(a);
}
//在这里定义的参数类型兼容实际的参数类型
log = log1;
function log2(a:number|string|boolean){
console.log(a);
}
//在这里实际的参数类型兼容定义的参数类型
log = log2;
8.6 泛型的兼容性 #
- 泛型在判断兼容性的时候会先判断具体的类型,然后再进行兼容性判断
//接口内容为空没用到泛型的时候是可以的
interface Empty<T>{}
let x:Empty<string>;
let y:Empty<number>;
x = y;
//接口内容不为空的时候不可以
interface NotEmpty<T>{
data:T
}
let x1:NotEmpty<string>;
let y1:NotEmpty<number>;
x1 = y1;
interface NotEmptyString{
data:string
}
interface NotEmptyNumber{
data:number
}
let xx3:NotEmptyString;
let yy3:NotEmptyNumber;
xx3 = yy3;
8.7 枚举的兼容性 #
- 枚举类型与数字类型兼容,并且数字类型与枚举类型兼容
- 不同枚举类型之间是不兼容的
//数字可以赋给枚举
enum Colors {Red,Yellow}
let c:Colors;
c = Colors.Red;
c = 1;
c = '1';
//枚举值可以赋给数字
let n:number;
n = 1;
n = Colors.Red;
9.类型保护 #
- 类型保护就是一些表达式,他们在编译的时候就能通过类型信息确保某个作用域内变量的类型
- 类型保护就是能够通过关键字判断出分支中的类型
9.1 typeof 类型保护 #
function double(input:string|number|boolean){ if(typeof input === 'string'){ return input + input; }else { if(typeof input === 'number'){ return input*2; }else{ return !input; } } }
9.2 instanceof类型保护 #
class Animal{
name:string;
}
class Bird extends Animal{
swing:number
}
function getName(animal:Animal){
if(animal instanceof Bird){
console.log(animal.swing);
}else{
console.log(animal.name);
}
}
9.3 null保护 #
- 如果开启了
strictNullChecks选项,那么对于可能为null的变量不能调用它上面的方法和属性
function getFirstLetter(s:string|null){
//第一种方式是加上null判断
if(s == null){
return '';
}
//第二种处理是增加一个或的处理
s = s || '';
return s.charAt(0);
}
//它并不能处理一些复杂的判断,需要加链判断运算符
function getFirstLetter2(s:string|null){
function log(){
console.log(s!.trim());
}
s = s || '';
log();
return s.charAt(0);
}
9.4 链判断运算符 #
- 链判断运算符是一种先检查属性是否存在,再尝试访问该属性的运算符,其符号为 ?.
- 如果运算符左侧的操作数 ?. 计算为 undefined 或 null,则表达式求值为 undefined 。否则,正常触发目标属性访问,方法或函数调用。
a?.b; //如果a是null/undefined,那么返回undefined,否则返回a.b的值.
a == null ? undefined : a.b;
a?.[x]; //如果a是null/undefined,那么返回undefined,否则返回a[x]的值
a == null ? undefined : a[x];
a?.b(); // 如果a是null/undefined,那么返回undefined
a == null ? undefined : a.b(); //如果a.b不函数的话抛类型错误异常,否则计算a.b()的结果
a?.(); //如果a是null/undefined,那么返回undefined
a == null ? undefined : a(); //如果A不是函数会抛出类型错误
//否则 调用a这个函数
9.5 可辨识的联合类型 #
- 就是利用联合类型中的共有字段进行类型保护的一种技巧
- 相同字段的不同取值就是可辨识
interface WarningButton{
class:'warning',
text1:'修改'
}
interface DangerButton{
class:'danger',
text2:'删除'
}
type Button = WarningButton|DangerButton;
function getButton(button:Button){
if(button.class=='warning'){
console.log(button.text1);
}
if(button.class=='danger'){
console.log(button.text2);
}
}
9.6 in操作符 #
- in 运算符可以被用于参数类型的判断
interface Bird {
swing: number;
}
interface Dog {
leg: number;
}
function getNumber(x: Bird | Dog) {
if ("swing" in x) {
return x.swing;
}
return x.leg;
}
9.7 自定义的类型保护 #
- TypeScript 里的类型保护本质上就是一些表达式,它们会在运行时检查类型信息,以确保在某个作用域里的类型是符合预期的
- 要自定义一个类型保护,只需要简单地为这个类型保护定义一个函数即可,这个函数的返回值是一个类型谓词
- 类型谓词的语法为
parameterName is Type这种形式,其中parameterName必须是当前函数签名里的一个参数名`
interface Bird {
swing: number;
}
interface Dog {
leg: number;
}
//没有相同字段可以定义一个类型保护函数
function isBird(x:Bird|Dog): x is Bird{
return (<Bird>x).swing == 2;
return (x as Bird).swing == 2;
}
function getAnimal(x: Bird | Dog) {
if (isBird(x)) {
return x.swing;
}
return x.leg;
}
10. 类型变换 #
10.1 交叉类型 #
- 交叉类型(Intersection Types)表示将多个类型合并为一个类型
interface Bird{ name:string, fly():void } interface Person{ name:string, talk():void } type BirdPerson = Bird & Person; let p:BirdPerson={name:'zhufeng',fly(){},talk(){}}; p.fly; p.name p.talk;
10.2 typeof #
- 可以获取一个变量的类型
//先定义类型,再定义变量
type People = {
name:string,
age:number,
gender:string
}
let p1:People = {
name:'zhufeng',
age:10,
gender:'male'
}
//先定义变量,再定义类型
let p1 = {
name:'zhufeng',
age:10,
gender:'male'
}
type People = typeof p1;
function getName(p:People):string{
return p.name;
}
10.3 索引访问操作符 #
- 可以通过[]获取一个类型的子类型
interface Person{
name:string;
age:number;
job:{
name:string
};
interests:{name:string,level:number}[]
}
let FrontEndJob:Person['job'] = {
name:'前端工程师'
}
let interestLevel:Person['interests'][0]['level'] = 2;
10.4 keyof #
- 索引类型查询操作符
interface Person{
name:string;
age:number;
gender:'male'|'female';
}
//type PersonKey = 'name'|'age'|'gender';
type PersonKey = keyof Person;
function getValueByKey(p:Person,key:PersonKey){
return p[key];
}
let val = getValueByKey({name:'zhufeng',age:10,gender:'male'},'name');
console.log(val);
10.5 映射类型 #
- 在定义的时候用in操作符去批量定义类型中的属性
interface Person{
name:string;
age:number;
gender:'male'|'female';
}
//批量把一个接口中的属性都变成可选的
type PartPerson = {
[Key in keyof Person]?:Person[Key]
}
let p1:PartPerson={};
//也可以使用泛型
type Part<T> = {
[key in keyof T]?:T[key]
}
let p2:Part<Person>={};
10.6 内置工具类型 #
- TS 中内置了一些工具类型来帮助我们更好地使用类型系统
10.6.1 Partial #
- Partial 可以将传入的属性由非可选变为可选,具体使用如下:
type Partial<T> = { [P in keyof T]?: T[P] };
interface A {
a1: string;
a2: number;
a3: boolean;
}
type aPartial = Partial<A>;
const a: aPartial = {}; // 不会报错
10.6.2 Required #
- Required 可以将传入的属性中的可选项变为必选项,这里用了 -? 修饰符来实现。
/**
* Make all properties in T required
*/
type Required<T> = { [P in keyof T]-?: T[P] };
interface Person{
name:string;
age:number;
gender?:'male'|'female';
}
let p:Required<Person> = {
name:'zhufeng',
age:10,
//gender:'male'
}
10.6.3 Readonly #
- Readonly 通过为传入的属性每一项都加上 readonly 修饰符来实现。
/**
* Make all properties in T readonly
*/
type Readonly<T> = { readonly [P in keyof T]: T[P] };
interface Person{
name:string;
age:number;
gender?:'male'|'female';
}
let p:Readonly<Person> = {
name:'zhufeng',
age:10,
gender:'male'
}
p.age = 11;
10.6.4 Pick #
- Pick 能够帮助我们从传入的属性中摘取某一项返回
/**
* From T pick a set of properties K
*/
type Pick<T, K extends keyof T> = { [P in K]: T[P] };
interface Animal {
name: string;
age: number;
}
// 摘取 Animal 中的 name 属性
type AnimalSub = Pick<Animal, "name">; // { name: string; }
10.6.5 映射类型修饰符的控制 #
- TypeScript中增加了对映射类型修饰符的控制
- 具体而言,一个
readonly或?修饰符在一个映射类型里可以用前缀+或-来表示这个修饰符应该被添加或移除 - TS 中部分内置工具类型就利用了这个特性(Partial、Required、Readonly...),这里我们可以参考 Partial、Required 的实现
10.7 条件类型 #
- 在定义泛型的时候能够添加进逻辑分支,以后泛型更加灵活
10.7.1 定义条件类型 #
interface Fish{
name:string
}
interface Water{
name:string
}
interface Bird{
name:string
}
interface Sky{
name:string
}
//三元运算符
type Condition<T> = T extends Fish?Water:Sky;
let con:Condition<Fish> = {name:'水'};
10.7.2 条件类型的分发 #
interface Fish{
name:string
}
interface Water{
name1:string
}
interface Bird{
name:string
}
interface Sky{
name2:string
}
//三元运算符
type Condition<T> = T extends Fish?Water:Sky;
let con1:Condition<Fish|Water> = {name1:'水'};
let con2:Condition<Fish|Water> = {name2:'水'};
10.7.3 内置条件类型 #
- TS 在内置了一些常用的条件类型,可以在 lib.es5.d.ts 中查看:
Exclude<T, U> // 从 T 可分配给的类型中排除 U。
Extract<T, U> // 从 T 可分配的类型中提取 U。
NonNullable<T> // 从 T 中排除 null 和 undefined。
ReturnType<T> // 获取函数类型的返回类型。
InstanceType<T> // 获取构造函数类型的实例类型。
10.7.3.1 Exclude #
type E = Exclude<string|number,string>;
let e:E = 10;
10.7.3.2 Extract #
type E = Extract<string|number,string>;
let e:E = '1';
10.7.3.3 NonNullable #
type E = NonNullable<string|number|null|undefined>;
let e:E = null;
10.7.3.4 ReturnType #
function getUserInfo() {
return { name: "zhufeng", age: 10 };
}
// 通过 ReturnType 将 getUserInfo 的返回值类型赋给了 UserInfo
type UserInfo = ReturnType<typeof getUserInfo>;
const userA: UserInfo = {
name: "zhufeng",
age: 10
};
10.7.3.5 InstanceType #
class Person{
name:string;
constructor(name){
this.name = name;
}
getName(){console.log(this.name)}
}
type P = InstanceType<typeof Person>;
let p:P = {name:'zhufeng',getName(){}};