1.栈 #
栈者,存储货物或供旅客住宿的地方,可引申为仓库
1.1 数据结构中的栈 #
- 栈是一组数据的存放方式,特点是先进后出,后进先出
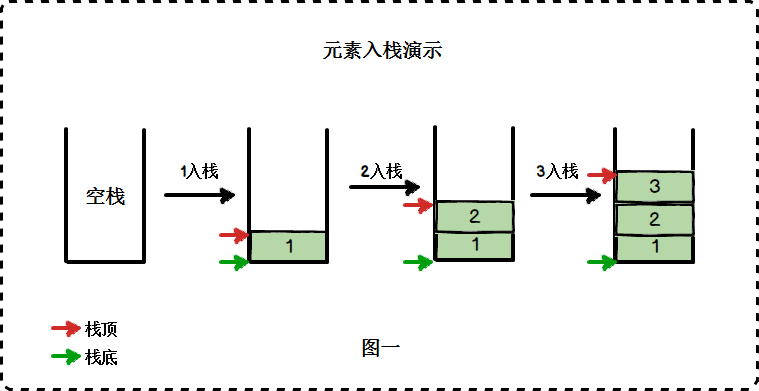
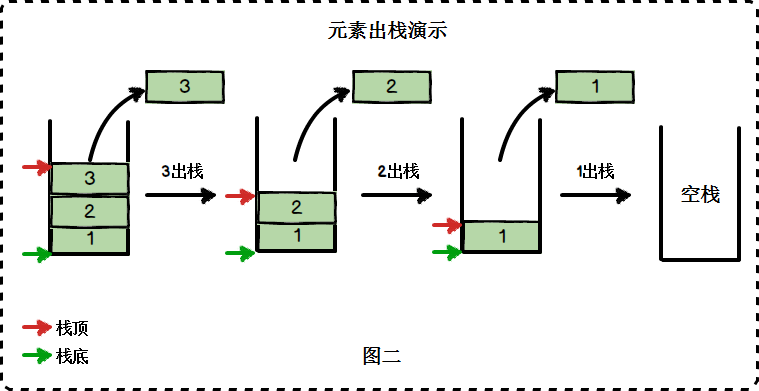
| 方法名 | 操作 |
|---|---|
| push() | 添加新元素到栈顶 |
| pop() | 移除栈顶的元素,同时返回被移除的元素 |
class Stack {
private items: number[] = [];
// 添加元素到栈顶,也就是栈的末尾
push(element: number) {
this.items.push(element);
}
// 栈的后进先出原则,从栈顶出栈
pop(): number {
return this.items.pop();
}
}
let stack = new Stack();
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
console.log(stack.pop());
1.2 代码的运行方式 #
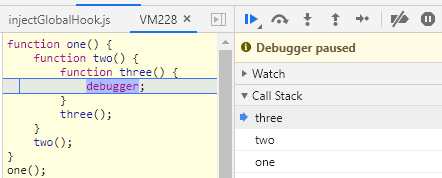
- 表示函数的一层层调用
function one() {
function two() {
function three() {
debugger;
}
three();
}
two();
}
one();
1.3 内存区域 #
- 栈也是是存放数据的一种内存区域
- 程序运行的时候,需要内存空间存放数据。一般来说,系统会划分出两种不同的内存空间:一种叫做stack(栈),另一种叫做heap(堆)
- stack是有结构的,每个区块按照一定次序存放,可以明确知道每个区块的大小
- heap是没有结构的,数据可以任意存放。因此,stack的寻址速度要快于heap
- 只要是局部的、占用空间确定的数据,一般都存放在stack里面,否则就放在heap里面,所有的对象都存放在heap
function task() {
var a = 1;
var b = 2;
var c = {
name: 'zhufeng',
age: 10
}
}
task();

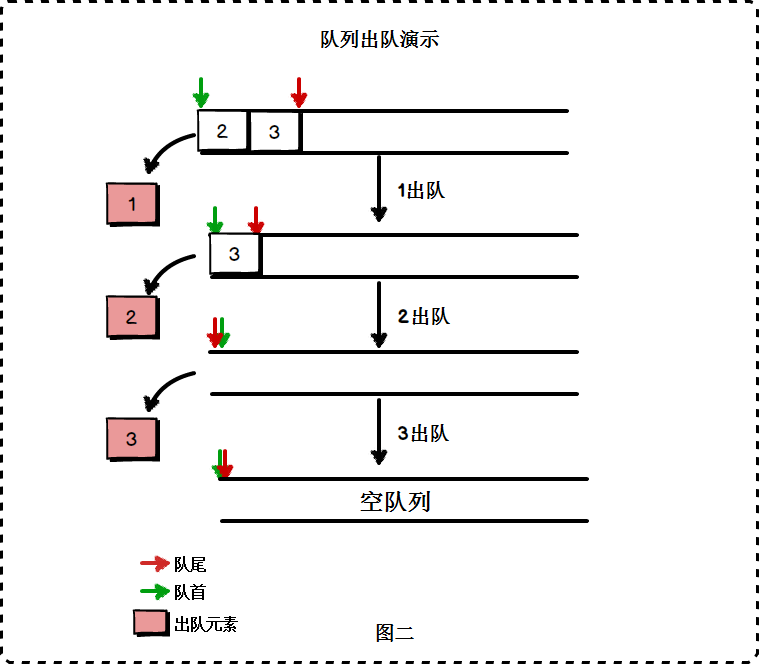
2. 队列 #
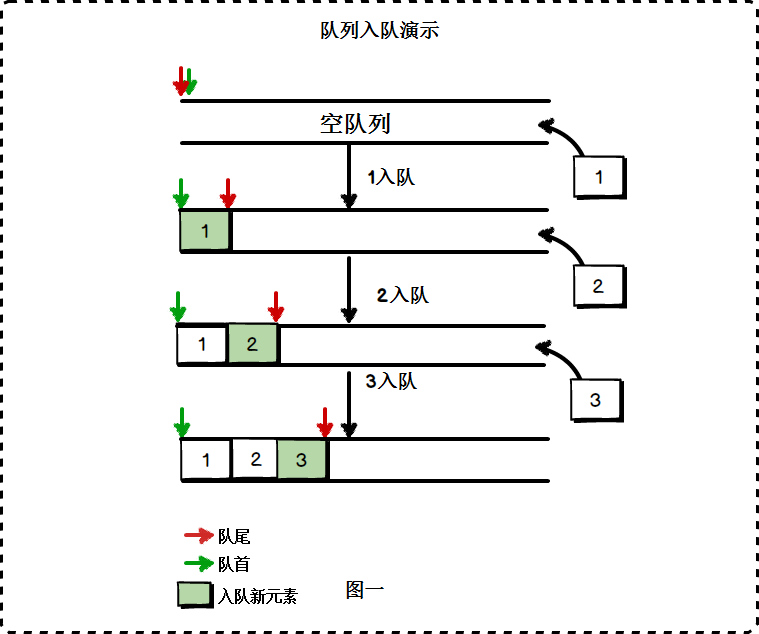
- 队列是一种操作受限制的线性表
- 特殊之处在于它只允许在表的前端进行删除操作,而在表的后端进行插入操作
- 进行插入操作的端称为队尾,进行删除操作的端称为队头
- 因为队列只允许在一端插入,在另一端删除,所以只有最早进入队列的元素才能最先从队列中删除,故队列又称为先进先出线性表
class Queue {
private items: number[] = [];
// 添加元素到栈顶,也就是栈的末尾
enqueue(element: number) {
this.items.push(element);
}
dequeue() {
return this.items.shift();
}
}
let queue = new Queue();
queue.enqueue(1);
queue.enqueue(2);
queue.enqueue(3);
console.log(queue.dequeue());//1
3. 数据类型 #
- JS中有七种基本数据类型
- 六种基本数据类型 Boolean Null Undefined Number String Symbol
- 一种引用类型 object {} [] /^$/ new Date() Math
| 类型 | 值 |
|---|---|
| Boolean | true或false |
| Null | null |
| Undefined | undefined |
| Number | 数字 |
| String | 字符串 |
| Symbol | 符号类型 |
4. 执行上下文 #
4.1 如何存储 #
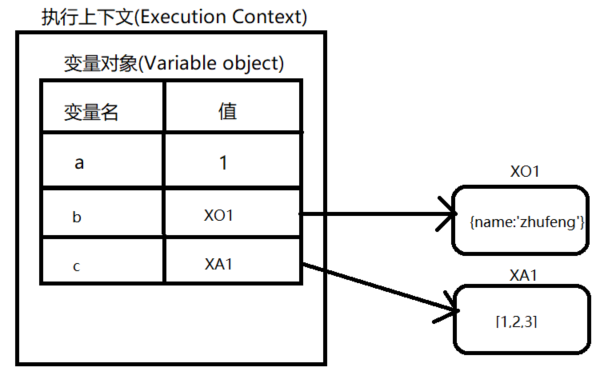
- 当函数运行时,会创建一个执行环境,这个执行环境就叫执行上下文(Execution Context)
- 执行上下文中会创建一个对象叫作变量对象(Value Object),基础数据类型都保存在变量对象中
- 引用数据类型的值保存在堆里,我们通过操作对象的引用地址来操作对象
function task(){
var a = 1;
var b = {
name:'zhufeng'
}
var c = [1,2,3];
}
let ExecuteContext = {
VO:{
a:1,
b:'XO1',
c:'XA1'
}
};
4.2 如何复制 #
4.2.1 基本数据 #
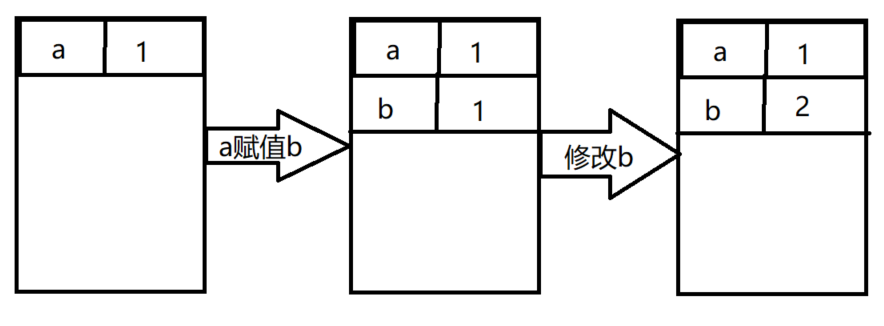
- 基本数据类型复制的是值本身
var a = 1;
var b = a;
b = 2;
console.log(a);
var ExecuteContext = {
VO: { a: 1 }
};
ExecuteContext.VO.b = ExecuteContext.VO.a;
ExecuteContext.VO.b = 2;
console.log(ExecuteContext.VO.a);
4.2.2 引用数据 #
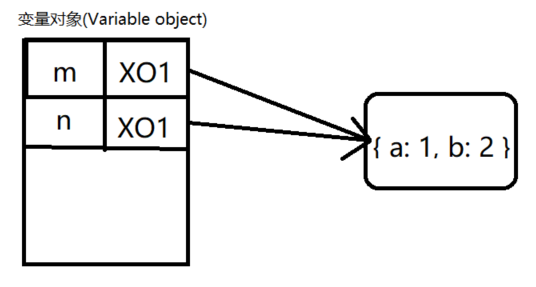
- 引用数据类型复制的是引用地址指针
var m = { a: 1, b: 2 };
var n = m;
n.a = 10;
console.log(m.a);
var ExecuteContext = {
VO: { m: { a: 1, b: 2 } }
};
ExecuteContext.VO.b = ExecuteContext.VO.a;
ExecuteContext.VO.a = 10;
console.log(ExecuteContext.VO.a);
5. 多个执行上下文栈 #
5.1 执行上下文分类 #
- JS代码在执行的时候会进入一个执行上下文,可以理解为当前代码的运行环境
- 在JS中运行环境主要分为全局执行上下文环境和函数环执行上下文环境
- 全局执行上下文只有一个,在客户端中一般由浏览器创建,也就是我们熟知的window对象,我们能通过this直接访问到它
- window对象还是var声明的全局变量的载体。我们通过var创建的全局对象,都可以通过window直接访问
5.2 多个执行上下文 #
- 在JS执行过程会产出多个执行上下文,JS引擎会有栈来管理这些执行上下文
- 执行上下文栈(下文简称执行栈)也叫调用栈,执行栈用于存储代码执行期间创建的所有上下文,具有LIFO(Last In First Out后进先出,也就是先进后出)的特性
- 栈底永远是全局上下文,栈顶为当前正在执行的上下文
- 当开启一个函数执行时会生成一个新的执行上下文并放入调用栈,执行完毕后会自动出栈
function one() {
var a = 1;
debugger;
function two() {
var b = 1;
debugger;
function three() {
var c = 1;
debugger;
}
three();
debugger;
}
two();
debugger;
}
one();
var globalExecuteContext = {
VO: { setTimeout: 'setTimeout' }
}
var executeContextStack = [globalExecuteContext];
var oneExecuteContext = {
VO: { a: 1 }
}
executeContextStack.push(oneExecuteContext);
var twoExecuteContext = {
VO: { b: 2 }
}
executeContextStack.push(twoExecuteContext);
var threeExecuteContext = {
VO: { c: 3 }
}
executeContextStack.push(threeExecuteContext);
console.log(executeContextStack);
executeContextStack.pop();
executeContextStack.pop();
executeContextStack.pop();
6. 执行上下文生命周期 #
6.1 生命周期有两个阶段 #
- 一个新的执行上下文的生命周期有两个阶段
- 创建阶段
- 创建变量对象
- 确定作用域链
- 确定
this指向
- 执行阶段
- 变量赋值
- 函数赋值
- 代码执行
- 创建阶段
6.2 变量对象 #
- 变量对象会保存变量声明(var)、函数参数(arguments)、函数定义(function)
- 变量对象会首先获得函数的参数变量和值
- 获取所有用
function进行的函数声明,函数名为变量对象的属性名,值为函数对象,如果属性已经存在,值会用新值覆盖 - 再依次所有的var关键字进行的变量声明,每找到一个变量声明,就会在变量对象上建一个属性,值为
undefined,如果变量名已经存在,则会跳过,并不会修改原属性值,let声明的变量并不会在此阶段进行处理
- 函数声明优先级更高,同名的函数会覆盖函数和变量,但同名
var变量并不会覆盖函数.执行阶段重新赋值可以改变原有的值
6.2.1 基本类型 #
console.log(a);
var a = 1;
var a = undefined;//变量提升
console.log(a);
a = 1;
6.2.2 变量提升 #
- 正常编写
var a = 1;
function fn(m) { console.log('fn'); }
function fn(m) { console.log('new_fn'); }
function a() { console.log('fn_a'); }
console.log(a);
fn(1);
var fn = 'var_fn';
console.log(fn);
//1
//new_fn
//var_fn
- 真正执行
// 创建阶段
function fn(m) { console.log('fn'); }
function fn(m) { console.log('new_fn'); }
function a() { console.log('fn_a'); }
var a = undefined;
var fn = undefined;
//执行阶段
a = 1;
console.log(a);
fn();
fn = 'var_fn';
console.log(fn);
- 上下文
// 创建阶段
var globalEC = {
VO: {
...arguments,
a: () => { console.log('fn_a'); },
fn: () => { console.log('new_fn'); }
}
}
var ECStack = [globalEC];
//执行阶段
globalEC.VO.a = 1;
console.log(globalEC.VO.a);
globalEC.VO.fn();
globalEC.VO.fn = 'var_fn';
console.log(globalEC.VO.fn);
6.2.3 激活对象 #
- 在函数的调用栈中,如果当前执行上下文处于函数调用栈的顶端,则意味着当前上下文处于激活状态,此时变量对象称为活动对象(AO,Activation Object) VO=>AO
- 活动变量包含变量对象所有的属性,并有包含
this指针
function one(m) {
function two() {
console.log('two');
}
}
one(1);
//执行阶段 VO=>AO
let VO = AO = {
m:1,
two: () => { console.log('two'); },
}
let oneEC={
VO,
this: window,
scopeChain:[VO,globalVO]
}
6.2.4 全局上下文的变量对象 #
- 在浏览器里,全局对象为
window - 全局上下文的变量对象为
window,而且这个变量对象不能激活变成活动对象 - 只在窗口打开,全局上下文会一直存在,所有的上下文都可以直接访问全局上下文变量对象上的属性
- 只有全局上下文的变量对象允许通过VO的属性名称来间接访问,在函数上下文中是不能直接访问VO对象的
- 未进入执行阶段前,变量对象中的属性都不能访问!但是进入到执行阶段之后,变量对象转变成了活动对象,里面的属性都能被访问了,对于函数上下文来讲,活动对象与变量对象其实都是同一个对象,只是处于执行上下文的不同生命周期
7. 作用域 #
7.1 作用域 #
- 在JS中,作用域是用来规定变量访问范围的规则
function one() {
var a = 1;
}
console.log(a);
7.2 作用域链 #
- 作用域链是由当前执行环境与上层执行环境的一系列变量对象组成的,它保证了当前执行环境对符合访问权限的变量和函数的有序访问
7.2.1 作用域链 #
function one() {
var a = 1;
function two() {
var b = 2;
function three() {
var c = 3;
console.log(a, b, c);
}
three();
}
two();
}
one();
// 1.创建全局上下文
var globalExecuteContextVO = { one: `()=>{var a = 1;}` }
var globalExecuteContext = {
VO: globalExecuteContextVO,
scopeChain: [globalExecuteContextVO]
}
var executeContextStack = [globalExecuteContext];
//2.执行one,创建one执行上下文
var oneExecuteContextVO = {
a: 1,
two: `()=>{var b = 2 ;}`
}
var oneExecuteContext = {
VO: oneExecuteContextVO,
scopeChain: [oneExecuteContextVO, globalExecuteContext.VO]
}
//2.执行two,创建two执行上下文
var twoExecuteContextVO = {
b: 2,
three: `()=>{var c = 3 ;}`
}
var twoExecuteContext = {
VO: twoExecuteContextVO,
scopeChain: [twoExecuteContextVO, oneExecuteContext.VO, globalExecuteContext.VO]
}
//3.执行three,创建three执行上下文
var threeExecuteContextVO = {
c: 3
}
var threeExecuteContext = {
VO: threeExecuteContextVO,
scopeChain: [threeExecuteContextVO, twoExecuteContext.VO, oneExecuteContext.VO, globalExecuteContext.VO]
}
function getValue(varName) {
for (let i = 0; i < threeExecuteContext.scopeChain.length; i++) {
if (varName in threeExecuteContext.scopeChain[i]) {
return threeExecuteContext.scopeChain[i][varName];
}
}
}
//console.log(a, b, c);
console.log(
getValue('a'),
getValue('b'),
getValue('c'),
);
7.2.2 作用域链 #
scopeChain其实是在创建函数的时候确定的
function one() {
var a = 1;
function two() {
console.log(a);
}
return two;
}
var a = 2;
var two = one();
two();
// 1.创建全局上下文
var globalExecuteContextVO = { one: `()=>{var a = 1;}`, a: undefined, two: undefined }
var globalExecuteContext = {
VO: globalExecuteContextVO,
scopeChain: [globalExecuteContextVO]
}
//2.开始执行
globalExecuteContextVO.a = 2;
//3.开始执行one
var oneExecuteContextVO = { a: undefined, two: `()=>{console.log(a)}` }
var oneExecuteContext = {
VO: oneExecuteContextVO,
scopeChain: [oneExecuteContextVO, globalExecuteContextVO]
}
oneExecuteContextVO.a = 1;
//4.给two赋值
globalExecuteContextVO.two = oneExecuteContextVO.two;
//5.执行two
var twoExecuteContextVO = {}
var twoExecuteContext = {
VO: twoExecuteContextVO,
//scopeChain是在创建此函数据的时候就决定了,跟在哪里执行无关
scopeChain: [twoExecuteContextVO, oneExecuteContextVO, globalExecuteContextVO]
}
8. 闭包 #
- 闭包有两部分组成,一个是当前的执行上下文A,一个是在该执行上下文中创建的函数B
- 当B执行的时候引用了当前执行上下文A中的变量就会产出闭包
- 当一个值失去引用的时候就会会标记,被垃圾收集回收机回收并释放空间
- 闭包的本质就是在函数外部保持内部变量的引用,从而阻止垃圾回收
- 调用栈的并不会影响作用域链,函数调用栈是在执行时才确定,而作用域规则是在代码编译阶段就已经确定了
- MDN定义:闭包是指这样的作用域
foo,它包含了一个函数fn,这个函数fn1可以调用被这个作用域所封闭的变量a、函数等内容
8.1 闭包 #
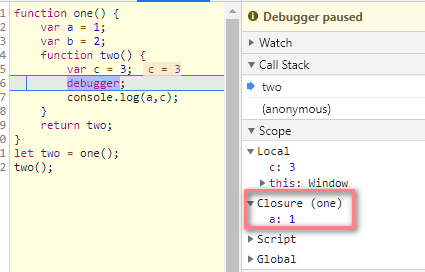
Call Stack为当前的函数调用栈Scope为当前正在被执行函数的作用域链Local为当前的活动对象
function one() {
var a = 1;
var b = 2;
function two() {
var c = 3;
debugger;
console.log(a,c);
}
return two;
}
let two = one();
two();
function one() {
var a = 1;
var b = 2;
function two() {
debugger;
console.log(a);
}
two();
}
one();
8.2 闭包优化 #
- 中间没用到的变量闭包会被忽略
function one() {
var a = 1;
function two() {
var b = 2;
function three() {
var c = 3;
debugger;
console.log(a, b, c);
}
three();
}
two();
}
one();
function one() {
var a = 1;
function two() {
var b = 2;
function three() {
var c = 3;
debugger;
console.log(a, c);
}
three();
}
two();
}
one();
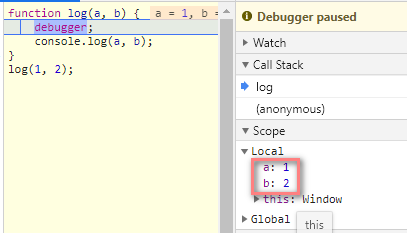
8.3 arguments #
function log(a, b) {
debugger;
console.log(a, b);
}
log(1, 2);
9. var和let #
- JS中作用域有:全局作用域、函数作用域。没有块作用域的概念。ECMAScript 6(简称ES6)中新增了块级作用域
- 块作用域由
{ }包括,if语句和for语句里面的{ }也属于块作用域
9.1 ES5问题 #
9.1.1 全局变量 #
- 在if或者for循环中声明的变量会变成全局变量
for(var i=0;i<=5;i++){ console.log("hello"); } console.log(i); //59.1.2 内层变量可能会覆盖外层变量 #
var a = 1; function fn() { console.log(a); if (false) { var a = 2; } } fn(); //undefined
9.2 let #
- 允许块级作用域任意嵌套
- 外层作用域无法读取内层作用域的变量
- 内层作用域可以定义外层作用域的同名变量
- 函数本身的作用域在其所在的块级作用域之内
'use strict'
function fn() {
console.log("out");
}
(function () {
if (false) {
function fn() {
console.log("in");
}
}
fn();
}());
9.3 var&let&const #
- var定义的变量没有块的概念,可以跨块访问,不能跨函数访问,有变量提升,可重复声明
- let定义的变量,只能在块作用域里访问,不能跨块访问,也不能跨函数访问,无变量提升,不可以重复声明
- let 声明的变量只在块级作用域内有效,不存在变量提升,而是绑定在暂时性死区
- 或者说let变量提升了,但是在let声明变量前不能使用该变量,这特性叫暂时性死区(temporal dead zone)
- 如果有重复变量
let会在编译阶段报错
9.3.1 暂时性死区 #
// 不存在变量提升
'use strict';
function func(){
console.log(i);
let i;
};
func(); // 报错
9.3.2 全局变量 #
- ES5声明变量只有两种方式:var和function
- ES6有let、const、import、class再加上ES5的var、function共有六种声明变量的方式
- 浏览器环境中顶层对象是window,Node中是global对象
- ES5中 顶层对象的属性等价于全局变量
- ES6中var、function声明的全局变量,依然是顶层对象的属性;let、const、class声明的全局变量不属于顶层对象的属性
9.3.3 题目 #
'use strict'
var a = 1;
console.log(a);//1
{
console.log(a);// f 1
function a() {
console.log(1);
}
}
console.log(a);// f 1
10. this #
- 当前函数的this是在被调用的时候才能确定的
- 如果当前的执行上下文处于调用栈的栈顶,这个时候变量对象变成了活动对象,THIS指针才能确定
10.1 全局对象 #
- 全局对象this指向本身
var a=1;//声明绑定变量对象,但在全局环境中,变量对象就是全局对象
this.b=2;//this绑定全局对象
c=3;//赋值操作 隐式绑定
10.1 用点调用 #
- 在一个函数上下文中,this由函数的调用者提供,由调用函数的方式来决定指向
- 如果是函数执行,如果前面有点,那么点前面是谁
this就是谁
let obj = {
getName(){
console.log(this);
}
};
obj.getName();
10.2 直接调用 #
- 如果没有,this就是window(严格模式下是undefined),自执行函数中的this一般都是window
- Strict_mode
let obj = {
getName(){
console.log(this);
}
};
let getName = obj.getName;
getName();
10.3 绑定事件 #
- 给元素绑定事件的时候,绑定的方法中的this一般是元素本身
container.addEventListener('click',function(){
console.log(this);
});
10.4 箭头函数 #
- 箭头函数没有自己的this
- 也没有prototype
- 也没有arguments
- 无法创建箭头函数的实例
let fn = () => {
console.log(this);
console.log(arguments);//Uncaught ReferenceError: arguments is not defined
}
console.log(fn.prototype);//undefined
fn();
new fn();//VM4416:8 Uncaught TypeError: fn is not a constructor
10.5 构造函数 #
- 构造函数中的THIS是当前类的实例
function fn(){
}
let obj = new fn();
10.6 call/apply/bind #
- call/apply/bind可以改变函数中this的指向
- 第一个参数是改变this指向(非严格模式下,传递null/undefined指向也是window)
- call参数是依次传递,apply是以数组的方式传递
!function (proto) {
function getContext(context) {
context = context || window;
var type = typeof context;
if (['number', 'string', 'boolean', 'null'].includes(type)) {
context = new context.constructor(context);
}
return context;
}
function call(context, ...args) {
context = getContext(context);
context._fn = this;
let result = context._fn(...args);
delete context._fn;
return result;
}
function apply(context, args) {
context = getContext(context);
context._fn = this;
let result = context._fn(...args);
delete context._fn;
return result;
}
function bind(context, ...bindArgs) {
return (...args) => this.call(context, ...bindArgs, ...args);
}
proto.call = call;
proto.apply = apply;
proto.bind = bind;
}(Function.prototype)
10.7 #
- 默认绑定
- 隐式绑定
- 显式绑定
- new绑定
- new > 显示 > 隐式 > 默认
隐式 > 默认
function one() {
console.log(this)
}
var obj = {
name: "obj",
one
}
obj.one()
显示 > 隐式
function one() {
console.log(this)
}
var obj = {
name: "obj",
one: one.bind("hello")
}
obj.one()
new > 显示
function one() {
console.log(this)
}
var helloOne = one.bind("hello")
var obj = new helloOne();
console.log(obj);
11. 面向对象 #
- 对象为无序属性的集合,其属性可以包含基本值、对象和函数
- Inheritance_and_the_prototype_chain
11.1 原型链 #
11.1.1 一切皆对象 #
- 对象就是一些属性的集合
- 方法也是一种属性
- 一切(引用类型)都是对象,对象是属性的集合
- 函数和数组也是对象
- 为什么
typeof function='function'
11.1.1.1 typeof #
- 检测数据类型
typeof返回的都是字符串 - 基本数据类型 number string boolean undefined symbol
- 引用类型 null {} [] /&$/ Date => object
console.log(typeof a); // undefined
console.log(typeof 1); // number
console.log(typeof 'zhufeng'); // string
console.log(typeof true); // boolean
console.log(typeof Symbol('a')); // symbol
console.log(typeof function () { }); //function
console.log(typeof [1, 2, 3]); //object
console.log(typeof { name: 'zhufeng' }); //object
console.log(typeof null); //object
console.log(typeof new Number(1)); //object
11.1.2 函数 #
- 对象是通过函数创建的
- 批量生产对象的函数
Object - 实现私有和公有属性的封装
let obj = new Object();
obj.name='zhufeng';
obj.age = 10;
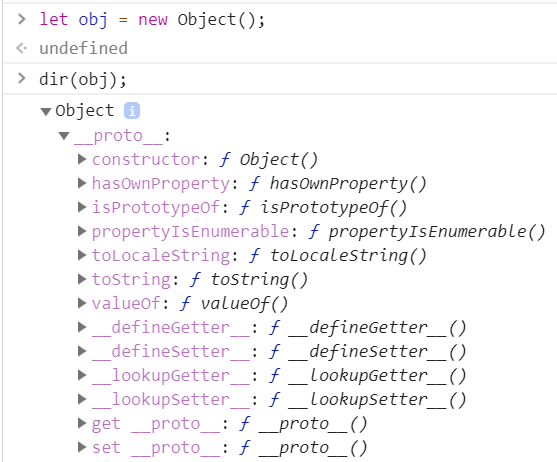
11.1.3 隐式原型 #
11.1.3.1 proto #
- 每个对象都有一个proto属性,指向创建该对象的函数的prototype
- Object.prototype
__proto__指向的是null
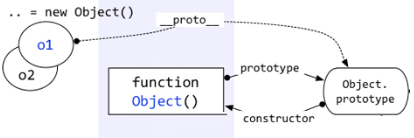
11.1.3.2 自定义函数的prototype #
- 自定义函数的
prototype的proto指向的就是Object.prototype
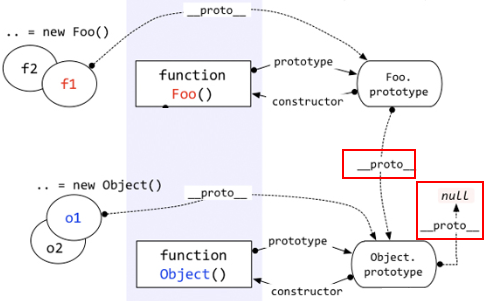
11.1.3.3 自定义函数 #
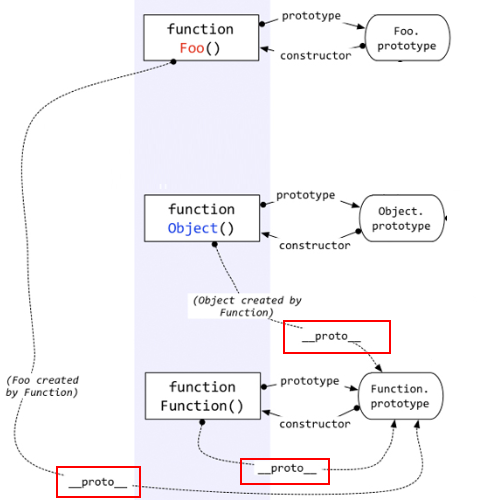
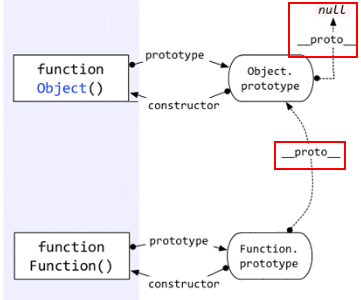
- 自定义函数Foo.proto指向Function.prototype
- Function的prototype和proto都指向
Function.prototype
let add = new Function('a','b','return a+b');
console.log(add(1,2));
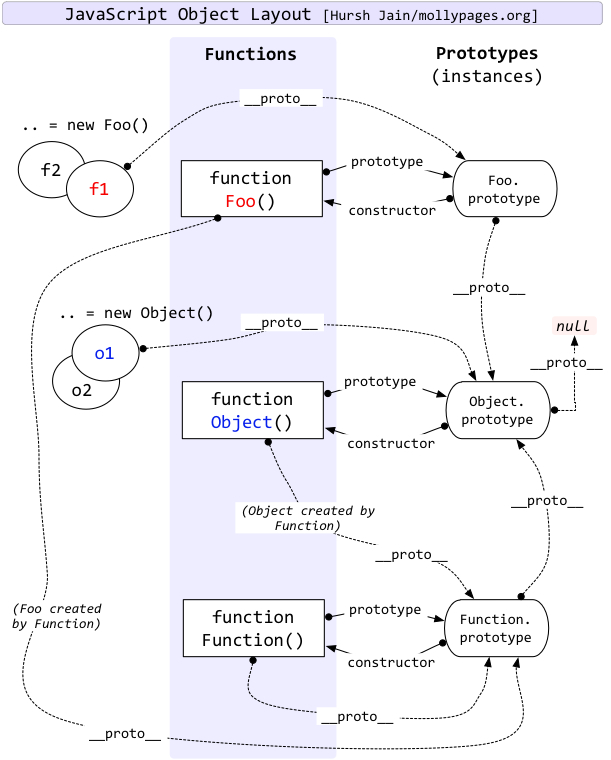
11.1.4 instanceof #
- instanceof运算符的第一个参数是一个对象,第二个参数一般是一个函数
- instanceof的判断规则是: 沿着对象的
__proto__这条链来向上查找找,如果能找到函数的prototype则返回true,否则 返回false
11.2 批量创建对象 #
- 通过
new来调用一个函数,这个函数就成为了构造函数,构造函数里可以对例对象的私有属性赋值 - 每个函数会有一个
prototype属性,此原型对象上存放所有实例的公有方法 - 若new的构造函数自己返回引用值,则以自己返回的为主,否则 返回创建的实例
- create
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
Person.prototype.getName = function () {
console.log(this.name);
}
let person = new Person('zhufeng');
person.getName();
Object.create = function (proto) {
function F() {}
F.prototype = proto;
return new F();
};
function _new(clazz, ...args) {
let _this = Object.create(clazz.prototype);
let result = clazz.call(_this, ...args);
if ((result != null && typeof result === 'object') || typeof result === 'function') {
return result;
}
return _this;
}
11.3 继承 #
class Father {
static staticFatherName = "FatherName"
static staticGetFatherName = function () {
console.log(Father.staticFatherName);
}
constructor(public name) {
this.name = name;
}
getName() {
console.log(this.name);
}
}
class Child extends Father {
static staticChildName = "ChildName"
static staticGetChildName = function () {
console.log(Child.staticChildName);
}
constructor(public name, public age) {
super(name);
this.age = age;
}
getAge() {
console.log(this.age);
}
}
let child = new Child('zhufeng', 10);
child.getName();
child.getAge();
Child.staticGetFatherName();
Child.staticGetChildName();
var _extends = (function () {
var extendStatics = function (Child, Father) {
return Object.setPrototypeOf(Child, Father);
}
return function (Child, Father) {
extendStatics(Child, Father);
function Temp() {
this.constructor = Child;
}
Temp.prototype = Father.prototype;
Child.prototype = new Temp();
};
})();
var Father = (function () {
function Father(name) {
this.name = name;
}
Father.prototype.getName = function () {
console.log(this.name);
};
Father.staticFatherName = "FatherName";
Father.staticGetFatherName = function () {
console.log(Father.staticFatherName);
};
return Father;
}());
//_super父类构造函数
var Child = (function (_super) {
_extends(Child, _super);
function Child(name, age) {
_super.call(this, name);//继承父类的实例私有属性
this.age = age;
return this;
}
Child.prototype.getAge = function () {
console.log(this.age);
};
Child.staticChildName = "ChildName";
Child.staticGetChildName = function () {
console.log(Child.staticChildName);
};
return Child;
}(Father));
let child = new Child('zhufeng', 10);
console.log(child);
child.getName();
child.getAge();
Child.staticGetFatherName();
Child.staticGetChildName();
var __extends = (this && this.__extends) || (function () {
var extendStatics = function (d, b) {
extendStatics = Object.setPrototypeOf ||
({ __proto__: [] } instanceof Array && function (d, b) { d.__proto__ = b; }) ||
function (d, b) { for (var p in b) if (b.hasOwnProperty(p)) d[p] = b[p]; };
return extendStatics(d, b);
};
return function (d, b) {
extendStatics(d, b);
function __() { this.constructor = d; }
d.prototype = b === null ? Object.create(b) : (__.prototype = b.prototype, new __());
};
})();
var Father = /** @class */ (function () {
function Father(name) {
this.name = name;
this.name = name;
}
Father.prototype.getName = function () {
console.log(this.name);
};
Father.staticFatherName = "FatherName";
Father.staticGetFatherName = function () {
console.log(Father.staticFatherName);
};
return Father;
}());
var Child = /** @class */ (function (_super) {
__extends(Child, _super);
function Child(name, age) {
var _this = _super.call(this, name) || this;
_this.name = name;
_this.age = age;
_this.age = age;
return _this;
}
Child.prototype.getAge = function () {
console.log(this.age);
};
Child.staticChildName = "ChildName";
Child.staticGetChildName = function () {
console.log(Child.staticChildName);
};
return Child;
}(Father));
var child = new Child('zhufeng', 10);
child.getName();
child.getAge();
Child.staticGetFatherName();
Child.staticGetChildName();
11.3.6 原型链面试题 #
- Operator_Precedence
function Foo() { getName = function () { console.log(1); } return this; } Foo.getName = function () { console.log(2); } Foo.prototype.getName = function () { console.log(3); } var getName = function () { console.log(4); } function getName() { console.log(5); } Foo.getName(); getName(); Foo().getName(); getName();//1 new Foo.getName(); new Foo().getName(); new new Foo().getName(); // 2 4 1 1 2 3 3
11.3.7 异步面试题 #
async function async1() {
console.log('async1 start')
await async2()
console.log('async1 end')
}
async function async2() {
console.log('async2')
}
console.log('script start')
setTimeout(function () {
console.log('setTimeout')
})
async1()
new Promise(function (resolve) {
console.log('promise1')
resolve()
}).then(function () {
console.log('promise2')
})
console.log('script end')
script start
async1 start
async2
promise1
script end
async1 end
promise2
setTimeout
12. ES6 #
- 词法环境VS静态作用域
- 变量环境(variableEnvironment)和词法环境(Lexical Environment)
- 闭包
12.1 词法环境 #
- let 原理
function fn() {
var a = 1;
let b = 2;
{
let b = 3;
var c = 4;
let d = 5;
//console.log(a, b, c, d);//TODO
}
{
let b = 6;
let d = 7;
//console.log(a, b, c, d);
}
}
fn();
/**
* 1.global编译阶段
*/
let globalEC = {
this: globalThis,
outer: null,//外部的执行上下文,词法作用域就是静态作用域,就是指作用域是由代码中函数声明的位置来决定的
variableEnvironment: {
fn() { console.log(a, b, c, d) }
},
lexicalEnvironment: {}
}
/**
* 2.fn编译阶段
*/
let fnEC = {
this: globalThis,
outer: globalEC,
variableEnvironment: { a: undefined, c: undefined },
lexicalEnvironment: [{ b: undefined }]
}
/**
* 3.编译代码块1
*/
fnEC.variableEnvironment.a = 1;
fnEC.lexicalEnvironment.b = 2;
fnEC.lexicalEnvironment.push({
b: undefined,
d: undefined
});
/**
* 4.执行代码块1
*/
fnEC.lexicalEnvironment[1].b = 3;
fnEC.variableEnvironment.c = 4;
fnEC.lexicalEnvironment[1].d = 5;
console.log(getValue('a', fnEC), getValue('b', fnEC), getValue('c', fnEC), getValue('d', fnEC));
function getValue(name, ec) {
for (let i = ec.lexicalEnvironment.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (name in ec.lexicalEnvironment[i]) {
return ec.lexicalEnvironment[i][name];
}
}
let currentVariableEnvironment = ec.variableEnvironment;
while (currentVariableEnvironment) {
if (name in currentVariableEnvironment) {
return currentVariableEnvironment[name];
}
currentVariableEnvironment = currentVariableEnvironment.outer;
}
return null;
}
/**
* 5.编译代码块2
*/
fnEC.lexicalEnvironment.pop();
fnEC.lexicalEnvironment.push({
b: undefined,
d: undefined
});
/**
* 5.执行代码块2
*/
fnEC.lexicalEnvironment[1].b = 6;
fnEC.lexicalEnvironment[1].d = 7;
console.log(getValue('a', fnEC), getValue('b', fnEC), getValue('c', fnEC), getValue('d', fnEC));
12.2 静态作用域 #
/* let name = 'zhufeng'
{
//ReferenceError: Cannot access 'name' before initialization
console.log(name)
let name = 'jiagou'
} */
function two() {
console.log(a);
}
function one() {
var a = 2;
two();
}
var a = 1;
one();
let globalEC = {
a: 1,
one() { },
two() { }
}
let twoEC = {
this: globalThis,
outer: globalEC,
variableEnvironment: { a: 1, two() { console.log(a) } } //出生的地方
}
var twoEc = { outer: globalEC };
console.log(twoEC.outer.a);
12.3 闭包 #
function one() {
var a = 1;
var name = 'one';
function two() {
var b = 2;
var name = 'two';
function three() {
var c = 3;
var name = 'three';
return () => console.log(a, b, c);
}
return three();
}
return two();
}
var fn = one();
fn();
let globalEC = {
this: globalThis,
outer: null,
variableEnvironment: { one() { } }
}
let oneEC = {
this: globalThis,
outer: globalEC.variableEnvironment,
variableEnvironment: { a: 1, two() { }, name: 'one' }
}
let twoEC = {
this: globalThis,
outer: oneEC.variableEnvironment,
variableEnvironment: { b: 2, three() { }, name: 'two' }
}
let threeEC = {
this: globalThis,
outer: twoEC.variableEnvironment,
variableEnvironment: { c: 3, name: 'three' }
}
let fnEC = {
this: globalThis,
outer: globalEC,
//Closure(three) Closure(two) Closure(one)
closures: [{ a: 1 }, { b: 2 }, { c: 3 }],
variableEnvironment: { c: 3 }
}
console.log(getValue('a', fnEC), getValue('b', fnEC), getValue('c', fnEC));
function getValue(name, ec) {
for (let i = ec.closures.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (name in ec.closures[i]) {
return ec.closures[i][name];
}
}
let currentVariableEnvironment = ec.variableEnvironment;
while (currentVariableEnvironment) {
if (name in currentVariableEnvironment) {
return currentVariableEnvironment[name];
}
currentVariableEnvironment = currentVariableEnvironment.outer;
}
return null;
}